2025-07-24 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's July LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
July LeetCoding Challenge 24
Description
Minimum Score After Removals on a Tree
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n where nums[i] represents the value of the ith node. You are also given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Remove two distinct edges of the tree to form three connected components. For a pair of removed edges, the following steps are defined:
- Get the XOR of all the values of the nodes for each of the three components respectively.
- The difference between the largest XOR value and the smallest XOR value is the score of the pair.
- For example, say the three components have the node values:
[4,5,7],[1,9], and[3,3,3]. The three XOR values are4 ^ 5 ^ 7 = 6,1 ^ 9 = 8, and3 ^ 3 ^ 3 = 3. The largest XOR value is8and the smallest XOR value is3. The score is then8 - 3 = 5.
Return the minimum score of any possible pair of edge removals on the given tree.
Example 1:
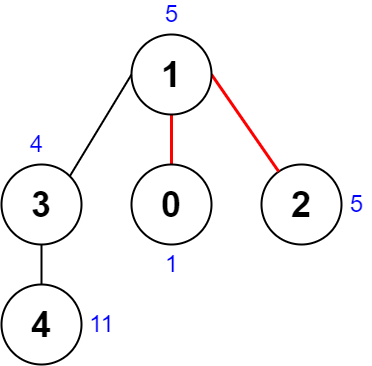
Input: nums = [1,5,5,4,11], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]] Output: 9 Explanation: The diagram above shows a way to make a pair of removals. - The 1st component has nodes [1,3,4] with values [5,4,11]. Its XOR value is 5 ^ 4 ^ 11 = 10. - The 2nd component has node [0] with value [1]. Its XOR value is 1 = 1. - The 3rd component has node [2] with value [5]. Its XOR value is 5 = 5. The score is the difference between the largest and smallest XOR value which is 10 - 1 = 9. It can be shown that no other pair of removals will obtain a smaller score than 9.
Example 2:
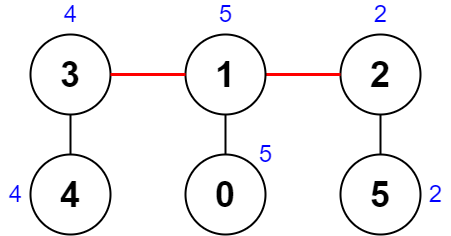
Input: nums = [5,5,2,4,4,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[5,2],[4,3],[1,3]] Output: 0 Explanation: The diagram above shows a way to make a pair of removals. - The 1st component has nodes [3,4] with values [4,4]. Its XOR value is 4 ^ 4 = 0. - The 2nd component has nodes [1,0] with values [5,5]. Its XOR value is 5 ^ 5 = 0. - The 3rd component has nodes [2,5] with values [2,2]. Its XOR value is 2 ^ 2 = 0. The score is the difference between the largest and smallest XOR value which is 0 - 0 = 0. We cannot obtain a smaller score than 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length3 <= n <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= 108edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biedgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
class Solution {
void dfs(
int current,
int parent,
const vector<int> &nums,
const vector<vector<int>> &neighbors,
vector<unordered_set<int>> &children,
vector<int> &xorValue
) {
xorValue[current] ^= nums[current];
children[current].insert(current);
for(auto next : neighbors[current]) {
if(next == parent) continue;
dfs(next, current, nums, neighbors, children, xorValue);
xorValue[current] ^= xorValue[next];
children[current].insert(children[next].begin(), children[next].end());
}
}
public:
int minimumScore(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> neighbors(n);
for(auto &e : edges) {
neighbors[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
neighbors[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
vector<unordered_set<int>> children(n);
vector<int> xorValue(n);
dfs(0, -1, nums, neighbors, children, xorValue);
// cout << xorValue << endl;
int totalXor = xorValue[0];
int answer = INT_MAX;
for(int i = 1; i < n - 1; ++i) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
int v1, v2, v3;
int xorI = xorValue[i];
int xorJ = xorValue[j];
if(children[i].count(j)) {
v1 = xorJ;
v2 = xorI ^ xorJ;
v3 = totalXor ^ xorI;
} else if(children[j].count(i)) {
v1 = xorI;
v2 = xorI ^ xorJ;
v3 = totalXor ^ xorJ;
} else {
v1 = xorI;
v2 = xorJ;
v3 = totalXor ^ xorI ^ xorJ;
}
answer = min(answer, max({v1, v2, v3}) - min({v1, v2, v3}));
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 65/65 cases passed (612 ms)
// Your runtime beats 27.77 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 18.25 % of cpp submissions (125.7 MB)