2025-01-18 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's January LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
January LeetCoding Challenge 18
Description
Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid
Given an m x n grid. Each cell of the grid has a sign pointing to the next cell you should visit if you are currently in this cell. The sign of grid[i][j] can be:
1which means go to the cell to the right. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i][j + 1])2which means go to the cell to the left. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i][j - 1])3which means go to the lower cell. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i + 1][j])4which means go to the upper cell. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i - 1][j])
Notice that there could be some signs on the cells of the grid that point outside the grid.
You will initially start at the upper left cell (0, 0). A valid path in the grid is a path that starts from the upper left cell (0, 0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1) following the signs on the grid. The valid path does not have to be the shortest.
You can modify the sign on a cell with cost = 1. You can modify the sign on a cell one time only.
Return the minimum cost to make the grid have at least one valid path.
Example 1:
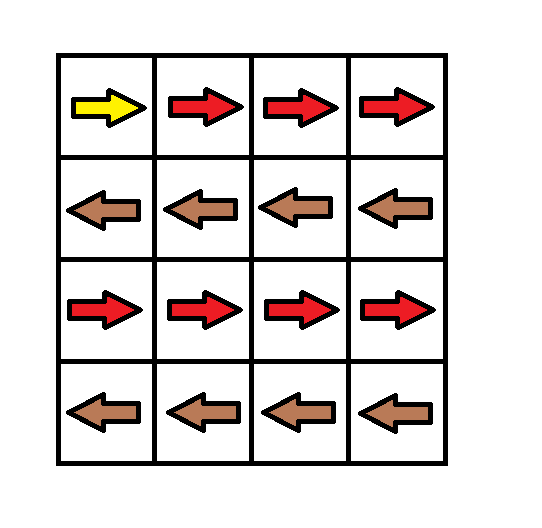
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]] Output: 3 Explanation: You will start at point (0, 0). The path to (3, 3) is as follows. (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (3, 3) The total cost = 3.
Example 2:
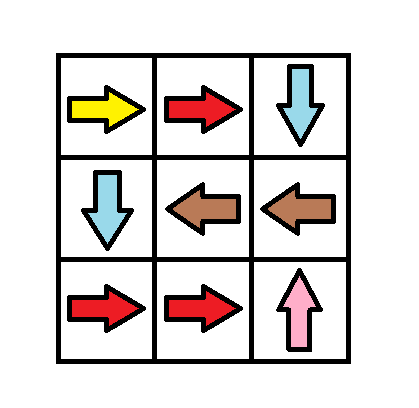
Input: grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]] Output: 0 Explanation: You can follow the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2).
Example 3:
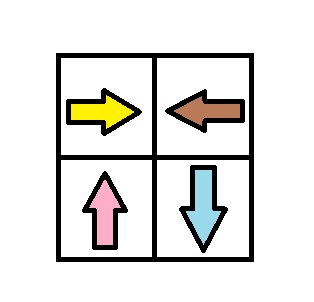
Input: grid = [[1,2],[4,3]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= grid[i][j] <= 4
Solution
class Solution {
const int MOVES[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
using pi = pair<int, int>;
public:
int minCost(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid.front().size();
vector<vector<pi>> neighbors(rows * cols);
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int pos = i * cols + j;
for(int m = 0; m < 4; ++m) {
int newRow = i + MOVES[m][0];
int newCol = j + MOVES[m][1];
if(newRow < 0 || newCol < 0 || newRow >= rows || newCol >= cols) continue;
int newPos = newRow * cols + newCol;
neighbors[pos].push_back({newPos, grid[i][j] != m + 1});
}
}
}
priority_queue<pi, vector<pi>, greater<pi>> pq;
pq.push({0, 0});
set<int> visited;
while(pq.size()) {
auto [cost, pos] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(pos == rows * cols - 1) return cost;
if(visited.count(pos)) continue;
visited.insert(pos);
for(auto [next, moveCost] : neighbors[pos]) {
pq.push({cost + moveCost, next});
}
}
return -1;
}
};
// Accepted
// 69/69 cases passed (173 ms)
// Your runtime beats 9 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 13.65 % of cpp submissions (46.7 MB)