2024-02-29 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's February LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
February LeetCoding Challenge 29
Description
Even Odd Tree
A binary tree is named Even-Odd if it meets the following conditions:
- The root of the binary tree is at level index
0, its children are at level index1, their children are at level index2, etc. - For every even-indexed level, all nodes at the level have odd integer values in strictly increasing order (from left to right).
- For every odd-indexed level, all nodes at the level have even integer values in strictly decreasing order (from left to right).
Given the root of a binary tree, return true if the binary tree is Even-Odd, otherwise return false.
Example 1:
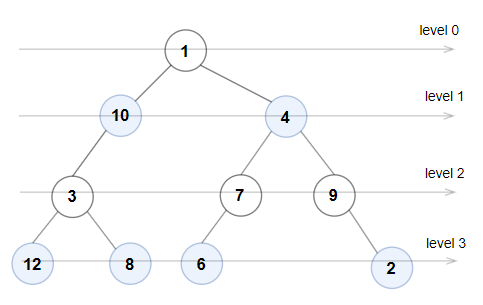
Input: root = [1,10,4,3,null,7,9,12,8,6,null,null,2] Output: true Explanation: The node values on each level are: Level 0: [1] Level 1: [10,4] Level 2: [3,7,9] Level 3: [12,8,6,2] Since levels 0 and 2 are all odd and increasing and levels 1 and 3 are all even and decreasing, the tree is Even-Odd.
Example 2:
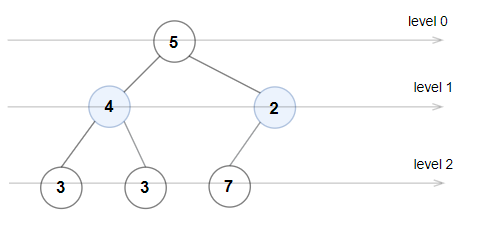
Input: root = [5,4,2,3,3,7] Output: false Explanation: The node values on each level are: Level 0: [5] Level 1: [4,2] Level 2: [3,3,7] Node values in level 2 must be in strictly increasing order, so the tree is not Even-Odd.
Example 3:
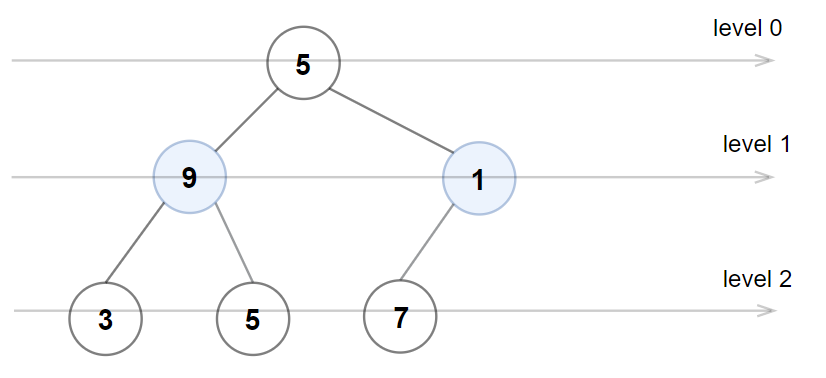
Input: root = [5,9,1,3,5,7] Output: false Explanation: Node values in the level 1 should be even integers.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 106
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
bool isEvenOddTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int level = 0;
while(q.size()) {
int sz = q.size();
int prev = (level % 2) ? INT_MAX : INT_MIN;
auto op = (level % 2) ? [](int a, int b){ return a <= b ;} : [](int a, int b){ return a >= b; };
for(int _ = 0; _ < sz; ++_) {
auto current = q.front();
q.pop();
if(current->val % 2 == level % 2) return false;
if(op(prev, current->val))return false;
prev = current->val;
if(current->left) q.push(current->left);
if(current->right) q.push(current->right);
}
level += 1;
}
return true;
}
};
// Accepted
// 106/106 cases passed (125 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 76.25 % of cpp submissions (149.2 MB)