2023-11-27 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's November LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
November LeetCoding Challenge 27
Description
Knight Dialer
The chess knight has a unique movement, it may move two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of an L). The possible movements of chess knight are shown in this diagaram:
A chess knight can move as indicated in the chess diagram below:
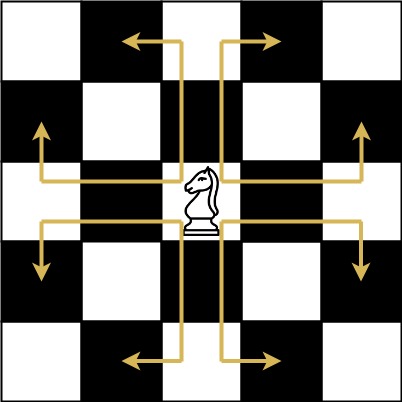
We have a chess knight and a phone pad as shown below, the knight can only stand on a numeric cell (i.e. blue cell).
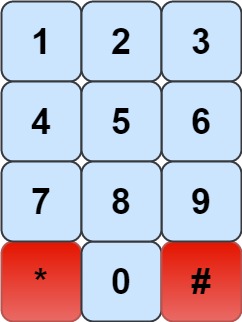
Given an integer n, return how many distinct phone numbers of length n we can dial.
You are allowed to place the knight on any numeric cell initially and then you should perform n - 1 jumps to dial a number of length n. All jumps should be valid knight jumps.
As the answer may be very large, return the answer modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1 Output: 10 Explanation: We need to dial a number of length 1, so placing the knight over any numeric cell of the 10 cells is sufficient.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2 Output: 20 Explanation: All the valid number we can dial are [04, 06, 16, 18, 27, 29, 34, 38, 40, 43, 49, 60, 61, 67, 72, 76, 81, 83, 92, 94]
Example 3:
Input: n = 3131 Output: 136006598 Explanation: Please take care of the mod.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5000
Solution
the problem is similar to the Fibonacci number, maybe we can rewrite it with matrix method, then we can calculate the answer when n is very large like 1e20.
class Solution {
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
public:
int knightDialer(int n) {
int ways[2][10];
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
ways[1][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
int parity = (i & 1);
ways[parity][0] = (ways[!parity][4] + ways[!parity][6]) % MOD;
ways[parity][1] = (ways[!parity][6] + ways[!parity][8]) % MOD;
ways[parity][2] = (ways[!parity][7] + ways[!parity][9]) % MOD;
ways[parity][3] = (ways[!parity][4] + ways[!parity][8]) % MOD;
ways[parity][4] = (ways[!parity][3] + ways[!parity][9]) % MOD;
ways[parity][4] = (ways[parity][4] + ways[!parity][0]) % MOD;
ways[parity][6] = (ways[!parity][1] + ways[!parity][7]) % MOD;
ways[parity][6] = (ways[parity][6] + ways[!parity][0]) % MOD;
ways[parity][7] = (ways[!parity][2] + ways[!parity][6]) % MOD;
ways[parity][8] = (ways[!parity][1] + ways[!parity][3]) % MOD;
ways[parity][9] = (ways[!parity][4] + ways[!parity][2]) % MOD;
ways[parity][5] = 0;
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
answer += ways[n & 1][i];
answer %= MOD;
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 121/121 cases passed (4 ms)
// Your runtime beats 97.08 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 98.68 % of cpp submissions (6.2 MB)