2023-06-29 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's June LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
June LeetCoding Challenge 29
Description
Shortest Path to Get All Keys
You are given an m x n grid grid where:
'.'is an empty cell.'#'is a wall.'@'is the starting point.- Lowercase letters represent keys.
- Uppercase letters represent locks.
You start at the starting point and one move consists of walking one space in one of the four cardinal directions. You cannot walk outside the grid, or walk into a wall.
If you walk over a key, you can pick it up and you cannot walk over a lock unless you have its corresponding key.
For some 1 <= k <= 6, there is exactly one lowercase and one uppercase letter of the first k letters of the English alphabet in the grid. This means that there is exactly one key for each lock, and one lock for each key; and also that the letters used to represent the keys and locks were chosen in the same order as the English alphabet.
Return the lowest number of moves to acquire all keys. If it is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
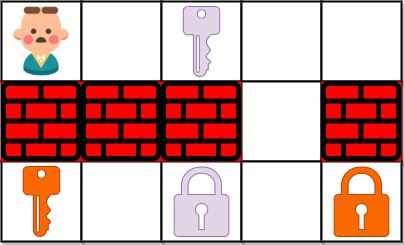
Input: grid = ["@.a..","###.#","b.A.B"] Output: 8 Explanation: Note that the goal is to obtain all the keys not to open all the locks.
Example 2:
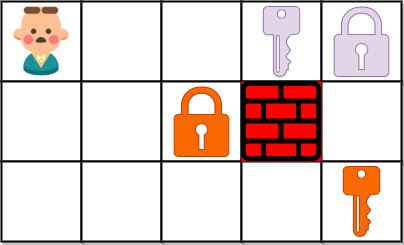
Input: grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"] Output: 6
Example 3:

Input: grid = ["@Aa"] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 30grid[i][j]is either an English letter,'.','#', or'@'.- The number of keys in the grid is in the range
[1, 6]. - Each key in the grid is unique.
- Each key in the grid has a matching lock.
Solution
const int MOVES[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
class Solution {
public:
int shortestPathAllKeys(vector<string>& grid) {
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid.front().size();
vector<set<int>> visit(rows * cols);
int startR;
int startC;
int keys = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
if(grid[i][j] == '@') {
startR = i;
startC = j;
} else if(islower(grid[i][j])) {
keys = max(keys, grid[i][j] - 'a' + 1);
}
}
}
int step = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, startR * cols + startC});
visit[startR * cols + startC].insert(0);
while(q.size()) {
int sz = q.size();
for(int _ = 0; _ < sz; ++_) {
auto [state, position] = q.front();
q.pop();
if(state == (1 << keys) - 1) return step;
int currentR = position / cols;
int currentC = position % cols;
for(int m = 0; m < 4; ++m) {
int newR = currentR + MOVES[m][0];
int newC = currentC + MOVES[m][1];
if(newR < 0 || newC < 0 || newR >= rows || newC >= cols) continue; // out of bound
if(grid[newR][newC] == '#') continue; // wall
if(isupper(grid[newR][newC]) && !(state & (1 << (grid[newR][newC] - 'A')))) continue; // lock without key
int newState = state;
int newPosition = newR * cols + newC;
if(islower(grid[newR][newC])) newState |= (1 << (grid[newR][newC] - 'a'));
if(visit[newPosition].count(newState)) continue; // visited
q.push({newState, newPosition});
visit[newPosition].insert(newState);
}
}
step += 1;
}
return -1;
}
};
// Accepted
// 35/35 cases passed (108 ms)
// Your runtime beats 51.68 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 55.37 % of cpp submissions (22.1 MB)