2023-06-16 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's June LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
June LeetCoding Challenge 16
Description
Number of Ways to Reorder Array to Get Same BST
Given an array nums that represents a permutation of integers from 1 to n. We are going to construct a binary search tree (BST) by inserting the elements of nums in order into an initially empty BST. Find the number of different ways to reorder nums so that the constructed BST is identical to that formed from the original array nums.
- For example, given
nums = [2,1,3], we will have 2 as the root, 1 as a left child, and 3 as a right child. The array[2,3,1]also yields the same BST but[3,2,1]yields a different BST.
Return the number of ways to reorder nums such that the BST formed is identical to the original BST formed from nums.
Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
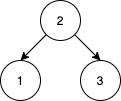
Input: nums = [2,1,3] Output: 1 Explanation: We can reorder nums to be [2,3,1] which will yield the same BST. There are no other ways to reorder nums which will yield the same BST.
Example 2:
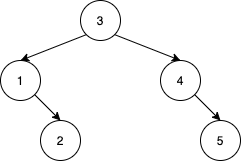
Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,2] Output: 5 Explanation: The following 5 arrays will yield the same BST: [3,1,2,4,5] [3,1,4,2,5] [3,1,4,5,2] [3,4,1,2,5] [3,4,1,5,2]
Example 3:
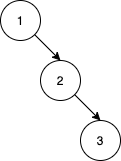
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no other orderings of nums that will yield the same BST.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= nums.length- All integers in
numsare distinct.
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
constexpr int qmul(int a, int b, int m) {
int result = 0;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) {
result += a;
result %= m;
}
a += a;
a %= m;
b >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
constexpr int qpow(int b, int e, int m) {
int result = 1;
while(e) {
if(e & 1) {
result = qmul(result, b, m);
}
b = qmul(b, b, m);
e >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
constexpr int inv(int a) {
return qpow(a, MOD - 2, MOD);
}
constexpr int C(int m, int n) {
int result = 1;
for(int i = max(m, n - m) + 1; i <= n; ++i) {
result = qmul(result, i, MOD);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= min(m, n - m); ++i) {
result = qmul(result, inv(i), MOD);
}
return result;
}
class Solution {
pair<int, int> children[1001];
int nodes[1001];
int len;
void constructTree(vector<int> &nums) {
len = nums.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= len; ++i) {
children[i] = {-1, -1};
nodes[i] = 1;
}
construct(nums, 0, INT_MIN, INT_MAX);
}
void construct(vector<int> &nums, int index, int leftBound, int rightBound) {
int root = nums[index];
bool left = false;
bool right = false;
// cout << root << ' ' << leftBound << ' ' << rightBound << endl;
for(int i = index + 1; i < nums.size() && !(left && right); i++) {
if(!left && nums[i] < root && nums[i] > leftBound) {
construct(nums, i, leftBound, min(rightBound, root));
children[root].first = nums[i];
nodes[root] += nodes[nums[i]];
left = true;
}
if(!right && nums[i] > root && nums[i] < rightBound) {
construct(nums, i, max(leftBound, root), rightBound);
children[root].second = nums[i];
nodes[root] += nodes[nums[i]];
right = true;
}
}
}
public:
int numOfWays(vector<int>& nums) {
constructTree(nums);
// for(int i = 1; i <= len; ++i) {
// cout << i << ": " << children[i].first << " " << children[i].second << ' ' << nodes[i] << endl;
// }
queue<int> q;
q.push(nums[0]);
int answer = 1;
while(q.size()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(children[cur].first != -1) {
q.push(children[cur].first);
if(children[cur].second != -1) {
answer = qmul(answer, C(nodes[children[cur].first], nodes[cur] - 1), MOD);
}
}
if(children[cur].second != -1) {
q.push(children[cur].second);
}
}
return (answer + MOD - 1) % MOD;
}
};
// Accepted
// 161/161 cases passed (396 ms)
// Your runtime beats 27.01 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 97.41 % of cpp submissions (13.1 MB)