2023-04-20 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's April LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
April LeetCoding Challenge 20
Description
Maximum Width of Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
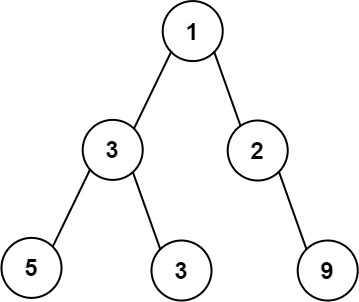
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
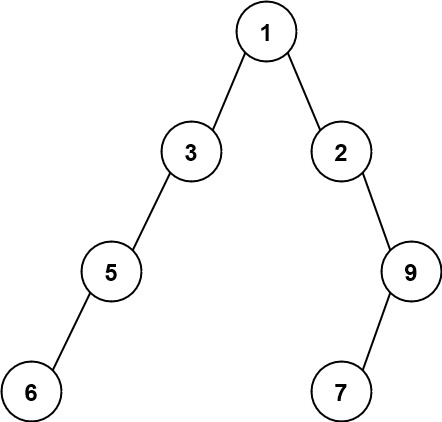
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,7] Output: 7 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the fourth level with length 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7).
Example 3:
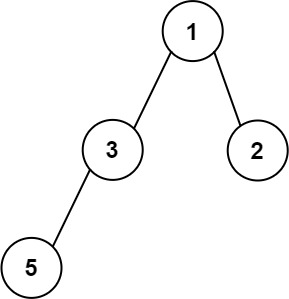
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width exists in the second level with length 2 (3,2).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
long long answer = 0;
queue<pair<long long, TreeNode*>> q;
q.push({0, root});
while(q.size()) {
int sz = q.size();
long long mmin = INT_MAX;
long long mmax = INT_MIN;
for(int _ = 0; _ < sz; ++_) {
auto [index, cur] = q.front();
mmin = min(index, mmin);
mmax = max(index, mmax);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push({index * 2 - mmin, cur->left});
if(cur->right) q.push({index * 2 + 1 - mmin, cur->right});
}
answer = max(answer, mmax - mmin + 1);
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 114/114 cases passed (7 ms)
// Your runtime beats 84.83 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 63.85 % of cpp submissions (17.4 MB)