2023-04-19 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's April LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
April LeetCoding Challenge 19
Description
Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
- Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
- Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
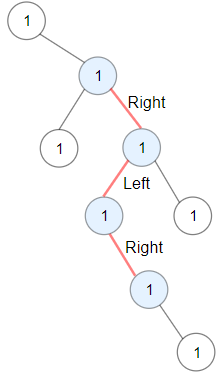
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1,null,1] Output: 3 Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2:
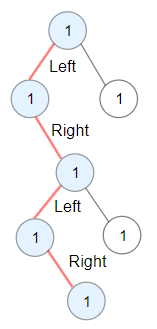
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1] Output: 4 Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
class Solution {
int answer = 0;
int solve(TreeNode *root, bool left) {
if(!root) return 0;
int r = solve(root->right, false);
int l = solve(root->left, true);
answer = max(answer, left + r);
answer = max(answer, !left + l);
if(left) return 1 + r;
else return 1 + l;
}
public:
int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
solve(root->left, true);
solve(root->right, false);
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 58/58 cases passed (163 ms)
// Your runtime beats 84.67 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 42.16 % of cpp submissions (100.4 MB)