2023-03-26 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's March LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
March LeetCoding Challenge 26
Description
Longest Cycle in a Graph
You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from node i, then edges[i] == -1.
Return the length of the longest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
Example 1:
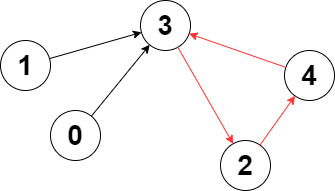
Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3] Output: 3 Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2. The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
Example 2:
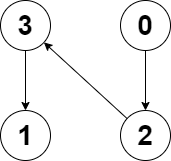
Input: edges = [2,-1,3,1] Output: -1 Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
Constraints:
n == edges.length2 <= n <= 105-1 <= edges[i] < nedges[i] != i
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int longestCycle(vector<int>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
if(n < 2) return -1;
vector<int> degree(n);
set<int> visit;
int answer = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(degree[i]) continue;
int current = i;
int prev;
int d = 1;
visit.clear();
while(current != -1) {
if(degree[current] && !visit.count(current)) break;
if(visit.count(current)) {
answer = max(answer, degree[prev] - degree[current] + 1);
break;
}
degree[current] = d;
d += 1;
visit.insert(current);
prev = current;
current = edges[current];
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 76/76 cases passed (554 ms)
// Your runtime beats 32.08 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 43.72 % of cpp submissions (153.5 MB)