2022-11-26 Daily Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's November LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
November LeetCoding Challenge 26
Description
Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
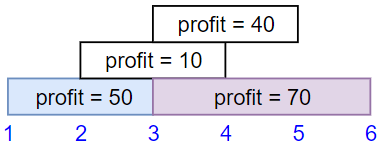
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
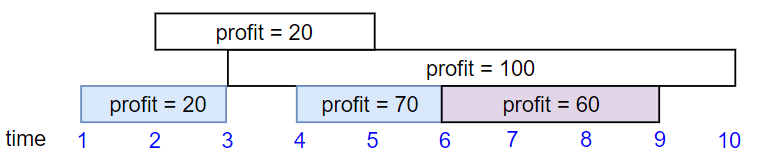
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
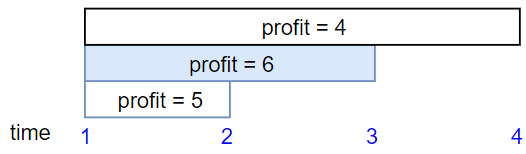
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
struct Job {
int start;
int end;
int profit;
Job() {}
Job(int start, int end, int profit): start(start), end(end), profit(profit) {}
bool operator<(const Job& other) const {
return this->start < other.start;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<Job> jobs;
int len = startTime.size();
for(int i = 0; i < startTime.size(); i++) {
jobs.push_back(Job(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]));
}
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
vector<int> dp(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
dp[i] = jobs[i].profit;
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(i) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i - 1] - jobs[i - 1].profit + jobs[i].profit);
}
int pos = lower_bound(jobs.begin() + i, jobs.end(), jobs[i].end,
[](const Job& j, int endTime) {
return j.start < endTime;
}) - jobs.begin();
if(pos < len && dp[pos] < dp[i] + jobs[pos].profit) dp[pos] = dp[i] + jobs[pos].profit;
}
return *max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end());
}
};
// Accepted
// 30/30 cases passed (83 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 83.93 % of cpp submissions (50 MB)