2022-09-24 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done leetcode's September LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
September LeetCoding Challenge 24
Description
Path Sum II
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return all root-to-leaf paths where the sum of the node values in the path equals targetSum. Each path should be returned as a list of the node values, not node references.
A root-to-leaf path is a path starting from the root and ending at any leaf node. A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
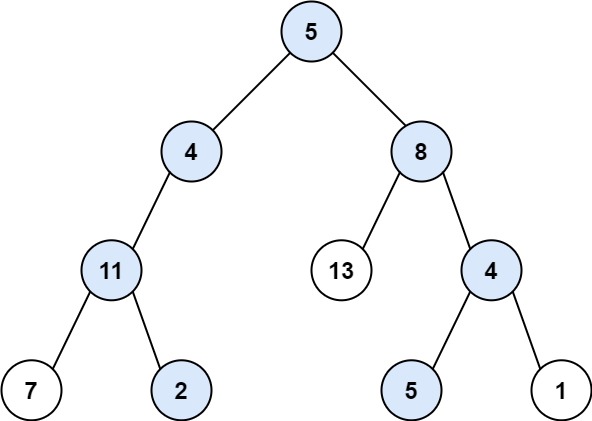
Input: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
Output: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
Explanation: There are two paths whose sum equals targetSum:
5 + 4 + 11 + 2 = 22
5 + 8 + 4 + 5 = 22
Example 2:

Input: root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Solution
class Solution {
void solve(
vector<vector<int>> &answer,
vector<int> &container,
TreeNode *root,
int rest
) {
if(!root) return;
container.push_back(root->val);
rest -= root->val;
if(!rest && !root->left && !root->right) {
answer.push_back(container);
} else {
solve(answer, container, root->left, rest);
solve(answer, container, root->right, rest);
}
container.pop_back();
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> answer;
vector<int> temp;
solve(answer, temp, root, targetSum);
return move(answer);
}
};
// Accepted
// 115/115 cases passed (0 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 81.42 % of cpp submissions (19.8 MB)