2021-09-09 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node and leetcode's September LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node
Description
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of ith node. The root of the tree is node 0. Find the kth ancestor of a given node.
The kth ancestor of a tree node is the kth node in the path from that node to the root node.
Implement the TreeAncestor class:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)Initializes the object with the number of nodes in the tree and the parent array.int getKthAncestor(int node, int k)return thekthancestor of the given nodenode. If there is no such ancestor, return-1.
Example 1:
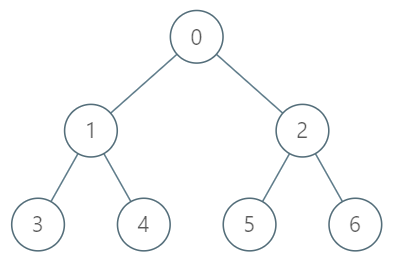
Input
["TreeAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor"]
[[7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [3, 1], [5, 2], [6, 3]]
Output
[null, 1, 0, -1]
Explanation
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 10^4parent.length == nparent[0] == -10 <= parent[i] < nfor all0 < i < n0 <= node < n- There will be at most
5 * 10^4queries.
Solution
failed to AC myself, amazing solution, brilliant!
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class TreeAncestor {
vector<vector<int>> dp;
public:
TreeAncestor(int n, vector<int>& parent) {
dp.resize(20, vector<int>(n + 1, -1));
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
dp[0][i] = parent[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i < 20; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
int xParent = dp[i - 1][j];
if(xParent == -1) {
dp[i][j] = -1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][xParent];
}
}
}
}
int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
for(int i = 0; i < 20 && node != -1; ++i) {
if(k & (1 << i)) {
node = dp[i][node];
}
}
return node;
}
};
// Accepted
// 16/16 cases passed (240 ms)
// Your runtime beats 98.19 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 89.46 % of cpp submissions (110.7 MB)
September LeetCoding Challenge 9
Description
Largest Plus Sign
You are given an integer n. You have an n x n binary grid grid with all values initially 1's except for some indices given in the array mines. The ith element of the array mines is defined as mines[i] = [xi, yi] where grid[xi][yi] == 0.
Return the order of the largest axis-aligned plus sign of 1*'s contained in* grid. If there is none, return 0.
An axis-aligned plus sign of 1's of order k has some center grid[r][c] == 1 along with four arms of length k - 1 going up, down, left, and right, and made of 1's. Note that there could be 0's or 1's beyond the arms of the plus sign, only the relevant area of the plus sign is checked for 1's.
Example 1:
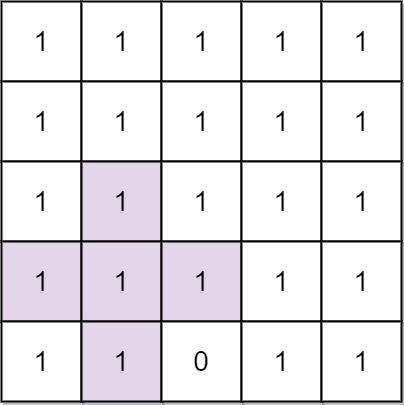
Input: n = 5, mines = [[4,2]]
Output: 2
Explanation: In the above grid, the largest plus sign can only be of order 2. One of them is shown.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1, mines = [[0,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no plus sign, so return 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= mines.length <= 50000 <= xi, yi < n- All the pairs
(xi, yi)are unique.
Solution
dumb questione
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
int orderOfLargestPlusSign(int n, vector<vector<int>>& mines) {
int left[n][n];
int up[n][n];
int right[n][n];
int down[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
left[i][j] = 1;
up[i][j] = 1;
right[i][j] = 1;
down[i][j] = 1;
}
}
for(auto &mine : mines) {
left[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;
up[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;
right[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;
down[mine[0]][mine[1]] = 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(left[i][j] && j) {
left[i][j] = left[i][j - 1] + 1;
}
if(up[i][j] && i) {
up[i][j] = up[i - 1][j] + 1;
}
}
}
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if(right[i][j] && j != n - 1) {
right[i][j] = right[i][j + 1] + 1;
}
if(down[i][j] && i != n - 1) {
down[i][j] = down[i + 1][j] + 1;
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
answer = max(answer, min({left[i][j], right[i][j], up[i][j], down[i][j]}));
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 56/56 cases passed (171 ms)
// Your runtime beats 82.12 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 89.94 % of cpp submissions (21.9 MB)