2021-09-03 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Majority Element II and leetcode's September LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Majority Element II
Description
Given an integer array of size n, find all elements that appear more than ⌊ n/3 ⌋ times.
Follow-up: Could you solve the problem in linear time and in O(1) space?
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,3]
Output: [3]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2]
Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 10^4-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int elements[2];
int count[2] = {};
for(auto c : nums) {
if(c == elements[0]) {
count[0] += 1;
} else if(c == elements[1]) {
count[1] += 1;
} else if(!count[0]) {
elements[0] = c;
count[0] = 1;
} else if(!count[1]) {
elements[1] = c;
count[1] = 1;
} else {
count[0] -= 1;
count[1] -= 1;
}
}
vector<int> answer;
for(auto candidate : elements) {
int count = 0;
for(auto i : nums) {
count += i == candidate;
}
if(count * 3 > nums.size()) {
answer.push_back(candidate);
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 82/82 cases passed (12 ms)
// Your runtime beats 73.07 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 46.99 % of cpp submissions (15.9 MB)
September LeetCoding Challenge 3
Description
Erect the Fence
You are given an array trees where trees[i] = [xi, yi] represents the location of a tree in the garden.
You are asked to fence the entire garden using the minimum length of rope as it is expensive. The garden is well fenced only if all the trees are enclosed.
Return the coordinates of trees that are exactly located on the fence perimeter.
Example 1:
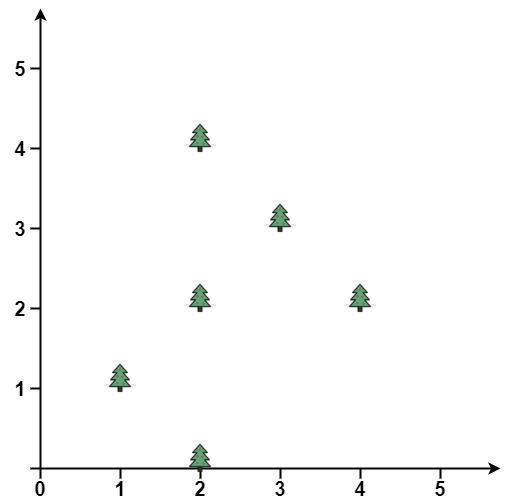
Input: points = [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[3,3],[2,4],[4,2]]
Example 2:
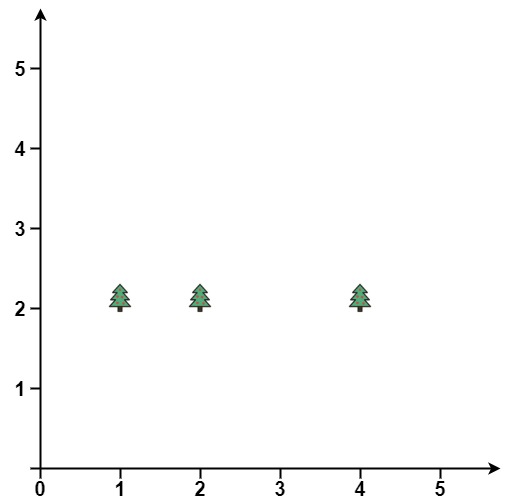
Input: points = [[1,2],[2,2],[4,2]]
Output: [[4,2],[2,2],[1,2]]
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 3000points[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 100- All the given points are unique.
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
struct Vector {
int x;
int y;
Vector(int x = 0, int y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
Vector(const vector<int> &v) : x(v[0]), y(v[1]) { }
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &os, const Vector &v) {
os << '(' << v.x << ',' << v.y << ')';
return os;
}
bool operator<(const Vector& v) const {
return this->x < v.x || (this->x == v.x && this->y < v.y);
}
Vector operator+(const Vector& v) const {
return Vector(this->x + v.x, this->y + v.y);
}
Vector operator-(const Vector& v) const {
return Vector(this->x - v.x, this->y - v.y);
}
};
int cross(const Vector& a, const Vector& b) {
return a.x * b.y - b.x * a.y;
}
int dot(const Vector& a, const Vector& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> outerTrees(vector<vector<int>>& treesVector) {
vector<Vector> trees;
for(const auto &tree : treesVector) {
trees.push_back(Vector(tree));
}
sort(trees.begin(), trees.end());
int len = trees.size();
int size = 1;
vector<int> st{0};
for(int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
while(size > 1 && cross(trees[st[size - 1]] - trees[st[size - 2]], trees[i] - trees[st[size - 1]]) < 0) {
st.pop_back();
size -= 1;
}
st.push_back(i);
size += 1;
}
int tmp = size;
for(int i = len - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
while(size > tmp && cross(trees[st[size - 1]] - trees[st[size - 2]], trees[i] - trees[st[size - 1]]) < 0) {
st.pop_back();
size -= 1;
}
st.push_back(i);
size += 1;
}
sort(st.begin(), st.end());
st.resize(unique(st.begin(), st.end()) - st.begin());
vector<vector<int>> answer;
for(auto i : st) {
answer.push_back({trees[i].x, trees[i].y});
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 84/84 cases passed (71 ms)
// Your runtime beats 62.22 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 76.3 % of cpp submissions (20.5 MB)