2021-09-02 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Spiral Matrix III and leetcode's September LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Spiral Matrix III
Description
You start at the cell (rStart, cStart) of an rows x cols grid facing east. The northwest corner is at the first row and column in the grid, and the southeast corner is at the last row and column.
You will walk in a clockwise spiral shape to visit every position in this grid. Whenever you move outside the grid's boundary, we continue our walk outside the grid (but may return to the grid boundary later.). Eventually, we reach all rows * cols spaces of the grid.
Return an array of coordinates representing the positions of the grid in the order you visited them.
Example 1:
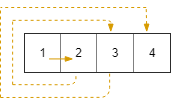
Input: rows = 1, cols = 4, rStart = 0, cStart = 0
Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]
Example 2:
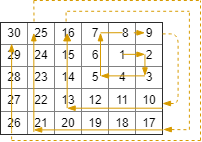
Input: rows = 5, cols = 6, rStart = 1, cStart = 4
Output: [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
Constraints:
1 <= rows, cols <= 1000 <= rStart < rows0 <= cStart < cols
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> spiralMatrixIII(int rows, int cols, int rStart, int cStart) {
int count = 0;
int moveX = 0;
int moveY = 1;
int dirMoves = 0;
int curMoves = 0;
vector<vector<int>> answer;
int rPos = rStart;
int cPos = cStart;
while(answer.size() < rows * cols) {
if(rPos < rows && rPos >= 0 && cPos < cols && cPos >= 0) {
answer.push_back({rPos, cPos});
}
rPos += moveX;
cPos += moveY;
curMoves += 1;
if(curMoves > dirMoves / 2) {
int newMoveX = moveY;
int newMoveY = -moveX;
moveX = newMoveX;
moveY = newMoveY;
curMoves = 0;
dirMoves += 1;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 73/73 cases passed (21 ms)
// Your runtime beats 17.53 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 54.02 % of cpp submissions (12.3 MB)
September LeetCoding Challenge 2
Description
Unique Binary Search Trees II
Given an integer n, return *all the structurally unique **BST'*s (binary search trees), which has exactly n nodes of unique values from 1 to n. Return the answer in any order.
Example 1:

Input: n = 3
Output: [[1,null,2,null,3],[1,null,3,2],[2,1,3],[3,1,null,null,2],[3,2,null,1]]
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 8
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
TreeNode *copy(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root) return nullptr;
return new TreeNode(root->val, copy(root->left), copy(root->right));
}
class Solution {
vector<TreeNode*> solve(int mask) {
if(!mask) return {nullptr};
vector<TreeNode*> answer;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
if(!(mask & (1 << i))) continue;
auto left = solve(mask & ((1 << i) - 1));
auto right = solve(mask & (((1 << 8) - 1) ^ ((1 << (i + 1)) - 1)));
for(auto l : left) {
for(auto r : right) {
answer.push_back(new TreeNode(i + 1, copy(l), copy(r)));
}
}
}
return answer;
}
public:
vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) {
return solve((1 << n) - 1);
}
};
// Accepted
// 8/8 cases passed (20 ms)
// Your runtime beats 39.86 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 5.85 % of cpp submissions (19.7 MB)