2021-08-28 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's August LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
LeetCode Review
Longest Uncommon Subsequence II
too easy to review
Verify Preorder Serialization of a Binary Tree
too easy to review
Sum of Square Numbers
too easy to review
Complex Number Multiplication
too easy to review
Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
too easy to review
Implement Stack using Queues
too easy to review
Design Circular Queue
too easy to review
Expressive Words
too easy to review
Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
too easy to review
Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
too easy to review
August LeetCoding Challenge 28
Description
Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
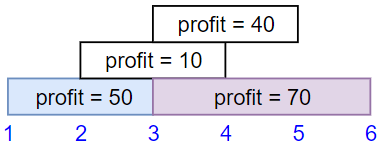
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70]
Output: 120
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job.
Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
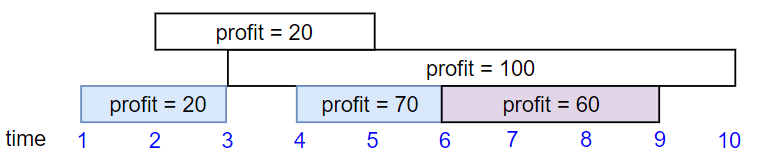
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60]
Output: 150
Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job.
Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
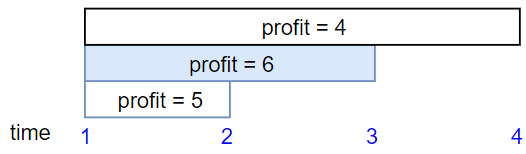
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4]
Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 10^41 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 10^91 <= profit[i] <= 10^4
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
struct Job {
int start;
int end;
int profit;
Job() {}
Job(int start, int end, int profit): start(start), end(end), profit(profit) {}
bool operator<(const Job& other) const {
return this->start < other.start;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<Job> jobs;
int len = startTime.size();
for(int i = 0; i < startTime.size(); i++) {
jobs.push_back(Job(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]));
}
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end());
vector<int> dp(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
dp[i] = jobs[i].profit;
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(i) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i - 1] - jobs[i - 1].profit + jobs[i].profit);
}
int pos = lower_bound(jobs.begin() + i, jobs.end(), jobs[i].end,
[](const Job& j, int endTime) {
return j.start < endTime;
}) - jobs.begin();
if(pos < len && dp[pos] < dp[i] + jobs[pos].profit) dp[pos] = dp[i] + jobs[pos].profit;
}
return *max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end());
}
};
// Accepted
// 27/27 cases passed (60 ms)
// Your runtime beats 99.91 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 77.26 % of cpp submissions (49.7 MB)