2021-08-08 Daily-Challenge
Today is Sunday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's August LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
LeetCode Review
Palindrome Partitioning II
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
bool isPalindrome(string &s, int start, int end) {
while(start < end) {
if(s[start++] != s[end--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
public:
int minCut(string s) {
int len = s.length();
if(isPalindrome(s, 0, len - 1)) return 0;
for(int i = 1; i < len - 1; ++i) {
if(isPalindrome(s, 0, i) && isPalindrome(s, i + 1, len - 1)) return 1;
}
vector<int> dp;
dp.push_back(-1);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
dp.push_back(i);
}
int pLen;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
pLen = 0;
while(i - pLen >= 0 && i + pLen < len && s[i - pLen] == s[i + pLen]) {
dp[i + pLen + 1] = min(dp[i + pLen + 1], dp[i - pLen] + 1);
pLen += 1;
}
pLen = 0;
while(i - pLen >= 0 && i + pLen + 1 < len && s[i - pLen] == s[i + pLen + 1]) {
dp[i + pLen + 2] = min(dp[i + pLen + 2], dp[i - pLen] + 1);
pLen += 1;
}
}
return dp.back();
}
};
// Accepted
// 33/33 cases passed (0 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 87.96 % of cpp submissions (6.5 MB)
August LeetCoding Challenge 8
Description
Rank Transform of a Matrix
Given an m x n matrix, return a new matrix answer where answer[row][col] is the rank of matrix[row][col].
The rank is an integer that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
-
The rank is an integer starting from
1. -
If two elements
pandqare in the same row or column, then:- If
p < qthenrank(p) < rank(q) - If
p == qthenrank(p) == rank(q) - If
p > qthenrank(p) > rank(q)
- If
-
The rank should be as small as possible.
It is guaranteed that answer is unique under the given rules.
Example 1:
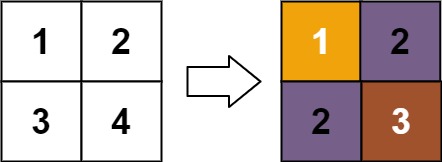
Input: matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: [[1,2],[2,3]]
Explanation:
The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column.
The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
Example 2:
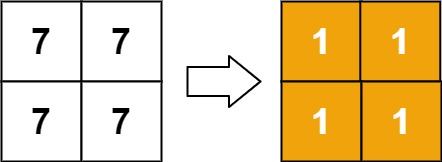
Input: matrix = [[7,7],[7,7]]
Output: [[1,1],[1,1]]
Example 3:
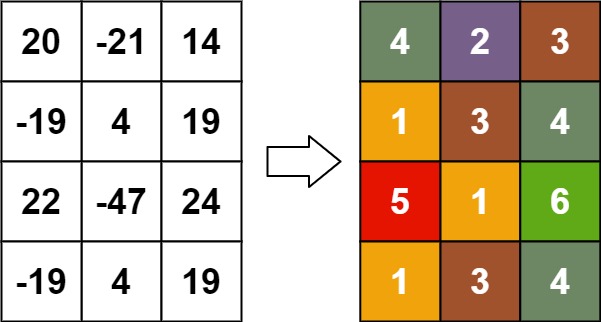
Input: matrix = [[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]]
Output: [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
Example 4:
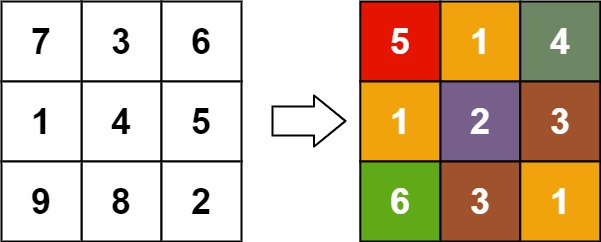
Input: matrix = [[7,3,6],[1,4,5],[9,8,2]]
Output: [[5,1,4],[1,2,3],[6,3,1]]
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500-10^9 <= matrix[row][col] <= 10^9
Solution
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
using pi = pair<int, int>;
class Solution {
int rows;
int cols;
vector<int> parents;
vector<int> maxRankInRow;
vector<int> maxRankInCol;
int find(int x) {
if(parents[x] != x) parents[x] = find(parents[x]);
return parents[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
int px = find(x);
int py = find(y);
parents[px] = parents[py];
}
void init(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
rows = matrix.size();
cols = matrix.front().size();
maxRankInRow.resize(rows, INT_MIN);
maxRankInCol.resize(cols, INT_MIN);
parents.resize(rows + cols);
vector<pi> vals;
sort(vals.begin(), vals.end(), greater<pi>());
}
void solveVal(
vector<vector<int>> &answer,
vector<pi> &positions
) {
for(int i = 0; i < rows + cols; ++i) {
parents[i] = i;
}
for(auto [row, col] : positions) {
merge(row, col + cols);
}
unordered_map<int, vector<pi>> groups;
for(auto [row, col] : positions) {
groups[find(row)].push_back({row, col});
}
for(auto &[_, group] : groups) {
int rank = 1;
for(auto [row, col] : group) {
rank = max(rank, max(maxRankInRow[row], maxRankInCol[col]) + 1);
}
for(auto [row, col] : group) {
answer[row][col] = rank;
maxRankInCol[col] = max(rank, maxRankInCol[col]);
maxRankInRow[row] = max(rank, maxRankInRow[row]);
}
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> matrixRankTransform(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
init(matrix);
priority_queue<pi, vector<pi>, greater<pi>> pq;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
pq.push({matrix[i][j], i * cols + j});
}
}
vector<vector<int>> answer(rows, vector<int>(cols));
vector<pi> sameVal;
int prev = INT_MIN;
while(pq.size()) {
auto [val, pos] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int row = pos / cols;
int col = pos % cols;
if(prev != val) {
solveVal(answer, sameVal);
sameVal.clear();
prev = val;
}
sameVal.push_back({row, col});
}
solveVal(answer, sameVal);
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 39/39 cases passed (344 ms)
// Your runtime beats 52.98 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 82.09 % of cpp submissions (75.4 MB)