2021-07-27 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Most Visited Sector in a Circular Track and leetcode's July LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Most Visited Sector in a Circular Track
Description
Given an integer n and an integer array rounds. We have a circular track which consists of n sectors labeled from 1 to n. A marathon will be held on this track, the marathon consists of m rounds. The ith round starts at sector rounds[i - 1] and ends at sector rounds[i]. For example, round 1 starts at sector rounds[0] and ends at sector rounds[1]
Return an array of the most visited sectors sorted in ascending order.
Notice that you circulate the track in ascending order of sector numbers in the counter-clockwise direction (See the first example).
Example 1:
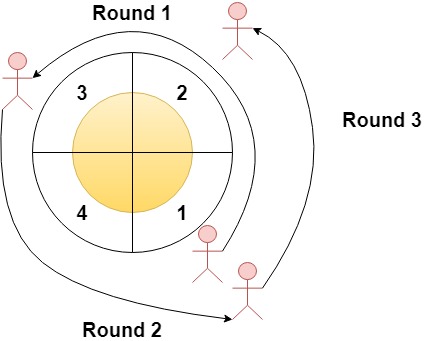
Input: n = 4, rounds = [1,3,1,2]
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The marathon starts at sector 1. The order of the visited sectors is as follows:
1 --> 2 --> 3 (end of round 1) --> 4 --> 1 (end of round 2) --> 2 (end of round 3 and the marathon)
We can see that both sectors 1 and 2 are visited twice and they are the most visited sectors. Sectors 3 and 4 are visited only once.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, rounds = [2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2]
Output: [2]
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, rounds = [1,3,5,7]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= m <= 100rounds.length == m + 11 <= rounds[i] <= nrounds[i] != rounds[i + 1]for0 <= i < m
Solution
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> mostVisited(int n, vector<int>& rounds) {
int more = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < rounds.size(); ++i) {
more += rounds[i] + n - rounds[i - 1];
}
more %= n;
vector<int> answer;
int begin = rounds.front();
for(int i = 0; i <= more; ++i) {
answer.push_back((begin + i + n - 1) % n + 1);
}
sort(answer.begin(), answer.end());
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 204/204 cases passed (4 ms)
// Your runtime beats 87.2 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 64.24 % of cpp submissions (11.2 MB)
July LeetCoding Challenge 28
Description
3Sum Closest
Given an array nums of n integers and an integer target, find three integers in nums such that the sum is closest to target. Return the sum of the three integers. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
Constraints:
3 <= nums.length <= 10^3-10^3 <= nums[i] <= 10^3-10^4 <= target <= 10^4
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int diff = INT_MAX;
int answer = -1;
int len = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < len-2; ++i) {
for(int j = i+1; j < len-1; ++j) {
if(j != i+1 && nums[j] == nums[j-1]) continue;
int tar = target-nums[i]-nums[j], start = j+1, end = len;
while(start < end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(nums[mid] > tar) {
if(nums[mid] - tar < diff) {
diff = nums[mid]-tar;
answer = nums[mid] + nums[i] + nums[j];
}
end = mid;
} else {
if(tar - nums[mid] < diff) {
diff = tar - nums[mid];
answer = nums[mid] + nums[i] + nums[j];
}
start = mid + 1;
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 131/131 cases passed (48 ms)
// Your runtime beats 10.58 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 60.68 % of cpp submissions (9.9 MB)
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int len = nums.size();
if(target <= nums.front() * 3 || len == 3) {
return nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
}
if(target >= nums.back() * 3) {
return nums[len - 1] + nums[len - 2] + nums[len - 3];
}
int diff = INT_MAX;
int answer = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < len - 2; ++i) {
if(nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] - target > diff) {
break;
}
int start = i + 1;
int end = len - 1;
while(start < end) {
int result = nums[i] + nums[start] + nums[end];
int d = result - target;
if(!d) {
return result;
} else if(d < 0) {
if(diff > -d) {
diff = -d;
answer = result;
}
do { start += 1; } while(start < end && nums[start] == nums[start - 1]);
} else {
if(diff > d) {
diff = d;
answer = result;
}
do { end -= 1; } while(start < end && nums[end] == nums[end + 1]);
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 131/131 cases passed (4 ms)
// Your runtime beats 97.91 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 11.39 % of cpp submissions (10 MB)