2021-07-26 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Shuffle String and leetcode's July LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Shuffle String
Description
Given a string s and an integer array indices of the same length.
The string s will be shuffled such that the character at the ith position moves to indices[i] in the shuffled string.
Return the shuffled string.
Example 1:
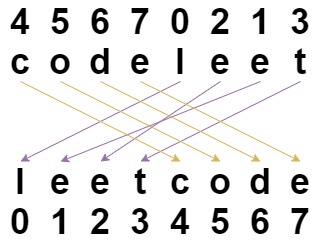
Input: s = "codeleet", indices = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3]
Output: "leetcode"
Explanation: As shown, "codeleet" becomes "leetcode" after shuffling.
Example 2:
Input: s = "abc", indices = [0,1,2]
Output: "abc"
Explanation: After shuffling, each character remains in its position.
Example 3:
Input: s = "aiohn", indices = [3,1,4,2,0]
Output: "nihao"
Example 4:
Input: s = "aaiougrt", indices = [4,0,2,6,7,3,1,5]
Output: "arigatou"
Example 5:
Input: s = "art", indices = [1,0,2]
Output: "rat"
Constraints:
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100scontains only lower-case English letters.0 <= indices[i] < n- All values of
indicesare unique (i.e.indicesis a permutation of the integers from0ton - 1).
Solution
class Solution {
public:
string restoreString(string s, vector<int>& indices) {
int len = s.length();
string answer(len, 'a');
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
answer[indices[i]] = s[i];
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 399/399 cases passed (8 ms)
// Your runtime beats 73.74 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 74.87 % of cpp submissions (15.2 MB)
July LeetCoding Challenge 27
Description
Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1:
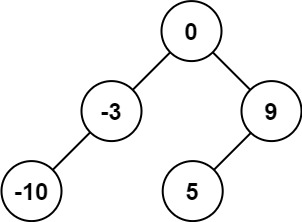
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:
Example 2:
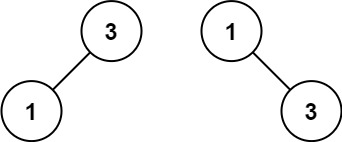
Input: nums = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Explanation: [1,3] and [3,1] are both a height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
Solution
class Solution {
TreeNode *construct(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end) {
if(begin > end) return nullptr;
int mid = (begin + end) >> 1;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = construct(nums, begin, mid - 1);
root->right = construct(nums, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
return construct(nums, 0, len - 1);
}
};
// Accepted
// 31/31 cases passed (8 ms)
// Your runtime beats 95.55 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 75.67 % of cpp submissions (21.4 MB)