2021-07-18 Daily-Challenge
Today is Sunday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's July LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
LeetCode Review
Number of Ways to Reorder Array to Get Same BST
amazing solution, what the heck? I still need time to investigation
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
#define MOD 1000000007
constexpr auto prefix = []{
array<int, 1002> arr{1, 1};
long long cur = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < 1002; ++i) {
cur = cur * i % MOD;
arr[i] = cur;
}
return arr;
}();
constexpr auto inv = []{
array<int, 1002> arr{0, 1};
for(int i = 2; i < 1002; ++i) {
arr[i] = ((long long)MOD - MOD / i) * arr[MOD % i] % MOD;
}
return arr;
}();
class Node {
public:
int size;
bool flag;
Node *l;
Node *r;
Node(int s = 1, Node* a = nullptr, Node* b = nullptr) :
size(s), flag(false), l(a), r(b) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
int numOfWays(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
Node p[len + 2];
for(int i = 0; i < len + 2; ++i) {
p[i].l = p + i - 1;
p[i].r = p + i + 1;
}
long long answer = prefix[len];
for(auto it = nums.rbegin(); it != nums.rend(); ++it) {
Node &cur = p[*it];
cur.flag = true;
if(cur.l->flag) {
cur.l->l->r = &cur;
cur.size += cur.l->size;
cur.l = cur.l->l;
}
if(cur.r->flag) {
cur.r->r->l = &cur;
cur.size += cur.r->size;
cur.r = cur.r->r;
}
if(cur.size > 1) answer = answer * inv[cur.size] % MOD;
// cout << answer << endl;
}
return (answer + MOD - 1) % MOD;
}
};
// Accepted
// 161/161 cases passed (4 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 97.55 % of cpp submissions (12.8 MB)
Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies
reverse topological sort
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
enum State { INIT, VISTED, STABLE };
class Solution {
State itemStates[30000];
State groupStates[30000];
int groupOrder[30000];
int count;
bool itemsTopologicalSort(
int child,
vector<int> &group,
vector<vector<int>> &beforeItems,
vector<vector<int>> &items,
vector<vector<int>> &beforeGroups
) {
if(itemStates[child] == State::VISTED) return false;
itemStates[child] = State::VISTED;
for(auto parent : beforeItems[child]) {
if(itemStates[parent] != State::STABLE) {
if(!itemsTopologicalSort(parent, group, beforeItems, items, beforeGroups)) return false;
}
if(group[parent] != group[child]) {
beforeGroups[group[child]].push_back(group[parent]);
}
}
itemStates[child] = State::STABLE;
items[group[child]].push_back(child);
return true;
}
bool groupTopologicalSort(
int child,
vector<vector<int>> &beforeGroups
) {
if(groupStates[child] == State::VISTED) return false;
groupStates[child] = State::VISTED;
for(auto parent : beforeGroups[child]) {
if(groupStates[parent] != State::STABLE) {
if(!groupTopologicalSort(parent, beforeGroups)) return false;
}
}
groupStates[child] = State::STABLE;
groupOrder[count++] = child;
return true;
}
public:
vector<int> sortItems(int n, int m, vector<int> &group, vector<vector<int>>& beforeItems) {
// init
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(group[i] == -1) group[i] = m++;
}
vector<vector<int>> items(m);
vector<vector<int>> beforeGroups(m);
bool ok = true;
for(int i = 0; i < n && ok; ++i) {
if(itemStates[i] == State::INIT) {
ok = itemsTopologicalSort(i, group, beforeItems, items, beforeGroups);
}
}
if(!ok) return {};
for(int i = 0; i < m && ok; ++i) {
if(groupStates[i] == State::INIT) {
ok = groupTopologicalSort(i, beforeGroups);
}
}
if(!ok) return {};
vector<int> answer;
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
int g = groupOrder[i];
answer.insert(answer.end(), items[g].begin(), items[g].end());
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 17/17 cases passed (40 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 97.29 % of cpp submissions (36.3 MB)
Valid Triangle Number
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
int triangleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int len = nums.size();
int answer = 0;
for(int i = upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0) - nums.begin(); i < len - 2; i++) {
int k = i + 2;
for(int j = i + 1; j < len - 1; ++j) {
while(k < len && nums[i] + nums[j] > nums[k]) k += 1;
answer += k - j - 1;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 233/233 cases passed (104 ms)
// Your runtime beats 52.79 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 19.41 % of cpp submissions (13.1 MB)
auto speedup = [](){
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
return 0;
}();
class Solution {
public:
int triangleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int count[1001] = {};
int prefix[1001] = {};
int mmax = -1;
for(auto i : nums) {
count[i] += 1;
if(i > mmax) mmax = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i < 1001; ++i) {
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1] + count[i];
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = mmax; i >= 1 ; --i) {
if(!count[i] || prefix[i] < 3) continue;
// cout << i << " ";
if(count[i] > 2) answer += count[i] * (count[i] - 1) * (count[i] - 2) / 6;
// cout << answer << ' ';
for(int j = i - 1; j; --j) {
if(!count[j] ) continue;
if(count[j] > 1 && j * 2 > i) {
answer += count[i] * count[j] * (count[j] - 1) / 2;
}
if(count[i] > 1 && i * 2 > j) {
answer += count[j] * count[i] * (count[i] - 1) / 2;
}
if(j - 1 > i - j) {
answer += (prefix[j - 1] - prefix[i - j]) * count[i] * count[j];
}
}
// cout << answer << endl;
}
return answer;
}
};
// Accepted
// 233/233 cases passed (12 ms)
// Your runtime beats 100 % of cpp submissions
// Your memory usage beats 19.41 % of cpp submissions (12.8 MB)
July LeetCoding Challenge 18
Description
Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
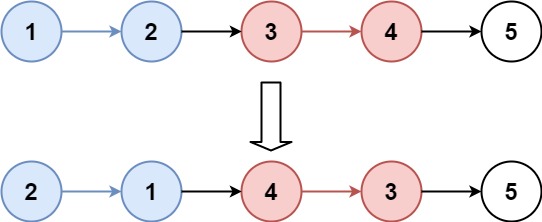
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
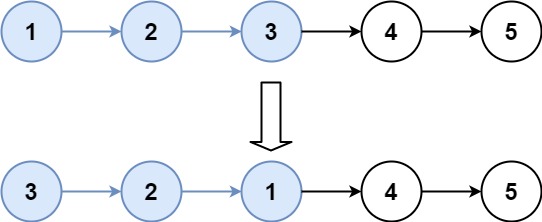
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1], k = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
sz. 1 <= sz <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= sz
Follow-up: Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
Solution
class Solution {
ListNode* reverseKNodes(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *tail = nullptr;
ListNode *next;
while(k--) {
next = head->next;
head->next = tail;
tail = head;
head = next;
}
return tail;
}
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *newTail = newHead;
while(cur) {
// cout << cur << ' ' << cur->val << endl;
bool longEnough = true;
ListNode *groupHead = cur;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
if(!cur) {
longEnough = false;
break;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(longEnough) {
newTail->next = reverseKNodes(groupHead, k);
while(newTail->next) newTail = newTail->next;
} else {
newTail->next = groupHead;
}
}
return newHead->next;
}
};