2021-07-03 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's July LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
LeetCode Review
Number of Ways to Stay in the Same Place After Some Steps
too easy to review
Construct the Lexicographically Largest Valid Sequence
too easy to review
Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array
too easy to review
Number of Dice Rolls With Target Sum
too easy to review
Capacity To Ship Packages Within D Days
too easy to review
Find K Closest Elements
using customized sorting
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findClosestElements(vector<int>& arr, int k, int x) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), [=](int a, int b) {
int da = abs(a - x);
int db = abs(b - x);
return da < db || (da == db && a < b);
});
vector<int> answer(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + k);
sort(answer.begin(), answer.end());
return answer;
}
};
binary search for left boundary
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findClosestElements(vector<int>& arr, int k, int x) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.size() - k;
while(left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if(x - arr[mid] > arr[mid + k] - x) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return vector<int>(arr.begin() + left, arr.begin() + left + k);
}
};
Gray Code
too easy to review
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
too easy to review
Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String
too easy to review
Max Consecutive Ones III
auto speedup = []() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
return nullptr;
}();
class Solution {
public:
int longestOnes(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int s = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
int len = nums.size();
if(s + k >= len) return len;
int start = -1;
int flip = 0;
int answer = 0;
for(int end = 0; end < len; ++end) {
if(!nums[end]) {
if(!k) {
start = end;
} else if(flip < k) {
flip += 1;
} else {
start += 1;
while(nums[start]) start += 1;
}
}
answer = max(answer, end - start);
}
return answer;
}
};
July LeetCoding Challenge 3
Description
Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than K
Given an m x n matrix matrix and an integer k, return the max sum of a rectangle in the matrix such that its sum is no larger than k.
It is guaranteed that there will be a rectangle with a sum no larger than k.
Example 1:
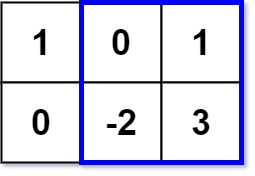
Input: matrix = [[1,0,1],[0,-2,3]], k = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: Because the sum of the blue rectangle [[0, 1], [-2, 3]] is 2, and 2 is the max number no larger than k (k = 2).
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[2,2,-1]], k = 3
Output: 3
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100-105 <= k <= 105
Follow up: What if the number of rows is much larger than the number of columns?
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int maxSumSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int k) {
int rows = matrix.size();
int cols = matrix.front().size();
// cout << "---------------" << endl;
vector<vector<int>> prefix(rows, vector<int>(cols + 1));
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
prefix[i][j + 1] = prefix[i][j] + matrix[i][j];
}
}
int answer = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < cols; ++i) {
for(int j = i + 1; j <= cols; ++j) {
set<int> tmp{0};
int sum = 0;
// cout << endl;
for(int row = 0; row < rows; ++row) {
sum += prefix[row][j] - prefix[row][i];
// cout << i << ' ' << j << ' ' << row << ' ' << sum << endl;
int diff = sum - k;
auto it = tmp.lower_bound(diff);
if(it != tmp.end()) {
answer = max(answer, sum - *it);
if(answer == k) return answer;
}
tmp.insert(sum);
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};