2021-05-06 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Jump Game VI and leetcode's May LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Jump Game VI
Description
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and an integer k.
You are initially standing at index 0. In one move, you can jump at most k steps forward without going outside the boundaries of the array. That is, you can jump from index i to any index in the range [i + 1, min(n - 1, i + k)] inclusive.
You want to reach the last index of the array (index n - 1). Your score is the sum of all nums[j] for each index j you visited in the array.
Return the maximum score you can get.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-1,-2,4,-7,3], k = 2
Output: 7
Explanation: You can choose your jumps forming the subsequence [1,-1,4,3] (underlined above). The sum is 7.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [10,-5,-2,4,0,3], k = 3
Output: 17
Explanation: You can choose your jumps forming the subsequence [10,4,3] (underlined above). The sum is 17.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,-5,-20,4,-1,3,-6,-3], k = 2
Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length, k <= 10^5-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4
Solution
monotonic queue
class Solution {
public:
int maxResult(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
deque<int> monoQueue{nums[0]};
int len = nums.size();
for(int i = 1; i < min(k, len); ++i) {
nums[i] += monoQueue.front();
while(monoQueue.size() && monoQueue.back() < nums[i]) monoQueue.pop_back();
monoQueue.push_back(nums[i]);
}
for(int i = k; i < len; ++i) {
nums[i] += monoQueue.front();
while(monoQueue.size() && monoQueue.back() < nums[i]) monoQueue.pop_back();
if(monoQueue.size() && monoQueue.front() == nums[i - k]) monoQueue.pop_front();
monoQueue.push_back(nums[i]);
}
return nums.back();
}
};
May LeetCoding Challenge 6
Description
Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
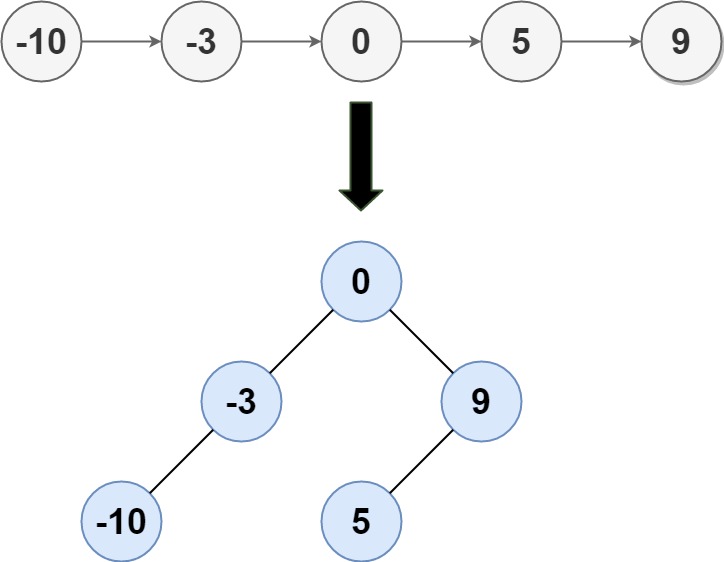
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Solution
done before
class Solution {
ListNode *cur;
int length(ListNode *head) {
int len = 0;
while(head) {
len += 1;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
TreeNode *buildBST(int begin, int end) {
if(begin > end) return nullptr;
int mid = (begin + end) >> 1;
TreeNode *left = buildBST(begin, mid - 1);
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(cur->val);
root->left = left;
cur = cur->next;
root->right = buildBST(mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
int len = length(head);
cur = head;
return buildBST(0, len-1);
}
};