2021-03-06 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's March LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
BTW, when I finish my Dota2 game, I realized that I've registered in Biweekly Contest 47, I should have solved at least three problems, but I misunderstood third problem... I think problem is to find subsequence, but it's actually substring, it's total another problem.
LeetCode Review
Majority Element II
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> majorityElement(vector<int>& nums) {
int candidates[2] = {INT_MAX, INT_MAX};
int count[2] = {0};
for(auto n : nums) {
if(candidates[0] == n) {
count[0] += 1;
} else if(candidates[1] == n) {
count[1] += 1;
} else if(count[0] == 0) {
candidates[0] = n;
count[0] = 1;
} else if(count[1] == 0) {
candidates[1] = n;
count[1] = 1;
} else {
count[0] -= 1;
count[1] -= 1;
}
}
vector<int> answer;
for(auto candidate : candidates) {
int count = 0;
for(auto n : nums) count += (n == candidate);
if(count > nums.size() / 3) answer.push_back(candidate);
}
return move(answer);
}
};
Closest Divisors
too easy to review
Accounts Merge
class Solution {
unordered_map<string, int> id;
unordered_map<int, string> name;
vector<int> parent;
int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
parent[find(y)] = find(x);
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> accountsMerge(vector<vector<string>>& accounts) {
int count = 0;
for(auto &account : accounts) {
for(int i = 1; i < account.size(); ++i) {
if(!id.count(account[i])) {
id[account[i]] = count++;
}
}
name[id[account[1]]] = account[0];
}
parent.resize(count);
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for(auto &account : accounts) {
for(int i = 2; i < account.size(); ++i) {
merge(id[account[1]], id[account[i]]);
}
}
vector<vector<string>> answer;
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
if(find(i) != i) continue;
vector<string> account{name[i]};
for(auto &[email, id] : id) if(find(id) == i) account.push_back(email);
sort(account.begin()+1, account.end());
answer.push_back(account);
}
return move(answer);
}
};
// 49 / 49 test cases passed.
// Status: Accepted
// Runtime: 84 ms
// Memory Usage: 31.7 MB
class Solution {
unordered_map<string, int> id;
vector<string> id2string;
unordered_map<int, string> name;
vector<int> parent;
int find(int x) {
if(parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
parent[find(y)] = find(x);
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> accountsMerge(vector<vector<string>>& accounts) {
int count = 0;
for(auto &account : accounts) {
for(int i = 1; i < account.size(); ++i) {
if(!id.count(account[i])) {
id[account[i]] = count++;
id2string.push_back(account[i]);
}
}
name[id[account[1]]] = account[0];
}
parent.resize(count);
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) parent[i] = i;
for(auto &account : accounts) {
for(int i = 2; i < account.size(); ++i) {
merge(id[account[1]], id[account[i]]);
}
}
vector<vector<string>> answer;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
tmp[find(i)].push_back(i);
}
for(auto [root, mails] : tmp) {
vector<string> account{name[root]};
for(auto id : mails) account.push_back(id2string[id]);
sort(account.begin() + 1, account.end());
answer.push_back(account);
}
return move(answer);
}
};
// 49 / 49 test cases passed.
// Status: Accepted
// Runtime: 80 ms
// Memory Usage: 35.2 MB
Map Sum Pairs
class MapSum {
map<string, int> mp;
public:
void insert(string key, int val) {
mp[key] = val;
}
int sum(string prefix) {
int result = 0;
bool found = false;
for(auto &[s, v] : mp) {
if(s.rfind(prefix, 0) == 0) {
found = true;
result += v;
} else {
if(found) break;
}
}
return result;
}
};
Matrix Diagonal Sum
too easy to review
Average of Levels in Binary Tree
too easy to review
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode*> st;
while(headA) {
st.insert(headA);
headA = headA->next;
}
while(headB) {
if(st.count(headB)) return headB;
headB = headB->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
// 46 / 46 test cases passed.
// Status: Accepted
// Runtime: 52 ms
// Memory Usage: 17.1 MB
Missing number
too easy to review
March LeetCoding Challenge 6
Description
Short Encoding of Words
A valid encoding of an array of words is any reference string s and array of indices indices such that:
words.length == indices.length- The reference string
sends with the'#'character. - For each index
indices[i], the substring ofsstarting fromindices[i]and up to (but not including) the next'#'character is equal towords[i].
Given an array of words, return the length of the shortest reference string s possible of any valid encoding of words.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["time", "me", "bell"]
Output: 10
Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "time#bell#" and indices = [0, 2, 5].
words[0] = "time", the substring of s starting from indices[0] = 0 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[1] = "me", the substring of s starting from indices[1] = 2 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[2] = "bell", the substring of s starting from indices[2] = 5 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
Example 2:
Input: words = ["t"]
Output: 2
Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "t#" and indices = [0].
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 20001 <= words[i].length <= 7words[i]consists of only lowercase letters.
Solution
we only need to check if one word is postfix of some other word.
reverse words then sort lexicographic order, if one word is postfix of some other word, that word must occur just after the word.
class Solution {
public:
int minimumLengthEncoding(vector<string>& words) {
for(auto &word : words) reverse(word.begin(), word.end());
sort(words.begin(), words.end());
int answer = 0;
int len = words.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
bool unique = true;
if(i < len - 1 && words[i + 1].rfind(words[i], 0) == 0) unique = false;
if(unique) answer += words[i].length() + 1;
}
return answer;
}
};
// You are here!
// Your runtime beats 100.00 % of cpp submissions.
// You are here!
// Your memory usage beats 94.00 % of cpp submissions.
Biweekly Contest 47
1779. Find Nearest Point That Has the Same X or Y Coordinate
You are given two integers, x and y, which represent your current location on a Cartesian grid: (x, y). You are also given an array points where each points[i] = [ai, bi] represents that a point exists at (ai, bi). A point is valid if it shares the same x-coordinate or the same y-coordinate as your location.
Return the index (0-indexed) of the valid point with the smallest Manhattan distance from your current location. If there are multiple, return the valid point with the smallest index. If there are no valid points, return -1.
The Manhattan distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2).
Example 1:
Input: x = 3, y = 4, points = [[1,2],[3,1],[2,4],[2,3],[4,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: Of all the points, only [3,1], [2,4] and [4,4] are valid. Of the valid points, [2,4] and [4,4] have the smallest Manhattan distance from your current location, with a distance of 1. [2,4] has the smallest index, so return 2.
Example 2:
Input: x = 3, y = 4, points = [[3,4]]
Output: 0
Explanation: The answer is allowed to be on the same location as your current location.
Example 3:
Input: x = 3, y = 4, points = [[2,3]]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are no valid points.
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 10^4points[i].length == 21 <= x, y, ai, bi <= 10^4
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int nearestValidPoint(int x, int y, vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int diff = INT_MAX;
int answer = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i) {
if(points[i][0] != x && points[i][1] != y) continue;
int dist = (points[i][0] - x) * (points[i][0] - x) + (points[i][1] - y) * (points[i][1] - y);
if(dist < diff) {
answer = i;
diff = dist;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
5681. Check if Number is a Sum of Powers of Three
Given an integer n, return true if it is possible to represent n as the sum of distinct powers of three. Otherwise, return false.
An integer y is a power of three if there exists an integer x such that y == 3x.
Example 1:
Input: n = 12
Output: true
Explanation: 12 = 31 + 32
Example 2:
Input: n = 91
Output: true
Explanation: 91 = 30 + 32 + 34
Example 3:
Input: n = 21
Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^7
Solution
class Solution {
vector<int> powers{4782969, 1594323, 531441, 177147, 59049, 19683, 6561, 2187, 729, 243, 81, 27, 9, 3, 1};
public:
bool checkPowersOfThree(int n) {
for(auto power : powers) {
if(n >= power) n -= power;
}
return n == 0;
}
};
5682. Sum of Beauty of All Substrings
The beauty of a string is the difference in frequencies between the most frequent and least frequent characters.
- For example, the beauty of
"abaacc"is3 - 1 = 2.
Given a string s, return the sum of beauty of all of its substrings.
Example 1:
Input: s = "aabcb"
Output: 5
Explanation: The substrings with non-zero beauty are ["aab","aabc","aabcb","abcb","bcb"], each with beauty equal to 1.
Example 2:
Input: s = "aabcbaa"
Output: 17
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 500sconsists of only lowercase English letters.
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int beautySum(string s) {
vector<int> count(26);
for(auto c : s) count[c - 'a'] += 1;
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 25; ++i) {
for(int j = i + 1; j < 26; ++j) {
cout << i << ' ' << j << ' ' << answer << endl;
for(int k = 1; k <= count[i]; ++k) {
for(int l = 1; l <= count[j]; ++l) {
int diff = abs(k - l);
if(diff == 0) continue;
int base = 1;
int mmin = min(k, l);
int mmax = max(k, l);
for(int another = j + 1; another < 26; ++another) {
if(count[another] >= mmin) base += min(mmax, count[another]) - mmin + 1;
}
answer += base * diff;
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};
5683. Count Pairs Of Nodes
You are given an undirected graph represented by an integer n, which is the number of nodes, and edges, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] which indicates that there is an undirected edge between ui and vi. You are also given an integer array queries.
The answer to the jth query is the number of pairs of nodes (a, b) that satisfy the following conditions:
a < bcntis strictly greater thanqueries[j], wherecntis the number of edges incident toaorb.
Return an array answers such that answers.length == queries.length and answers[j] is the answer of the jth query.
Note that there can be repeated edges.
Example 1:
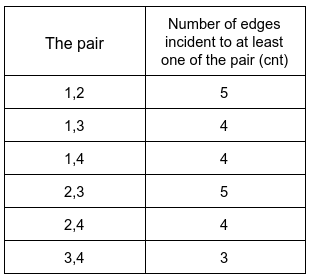
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[2,4],[1,3],[2,3],[2,1]], queries = [2,3]
Output: [6,5]
Explanation: The number of edges incident to at least one of each pair is shown above.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,5],[1,5],[3,4],[2,5],[1,3],[5,1],[2,3],[2,5]], queries = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [10,10,9,8,6]
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 2 * 10^41 <= edges.length <= 10^51 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi1 <= queries.length <= 200 <= queries[j] < edges.length
Solution
maintain a map which record every node pair with direct edges between them and number of edges, then maintain a sorted degree array. answering query follows these steps:
- for every node
i, find upper_bound ofquery - degree[i], then we know that right side of upper_bound is all we need for this node. Be careful, we only get candidates node pairs, becausedegree[i] + degree[j] >= cnt(i, j) = degree[i] + degree[j] - direct_edges[(i,j)] - iterate map, find if this pair is counted but is not answer, which means
degree[i] + degree[j] > querybutdegree[i] + degree[j] - direct_edges[(i,j)] <= query
time complexity analysis:
- maintain map: $O(E)$
- get degree and sort them: $O(E) + O(n\log n)$
- step 1: $O(n\log n)$ cause upper_bound is binary search
- step 2: $O(E)$, because there is at most $max(n^2, E)$ node pairs.
so the time complexity of whole solution is $O(n \log n) + O(E)$
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> countPairs(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& queries) {
struct p {
int a;
int b;
p (int a = 0, int b = 0): a(a), b(b){}
bool operator<(const p &other) const {
return this->a < other.a || (this->a == other.a && this->b < other.b);
}
};
map<p, int> direct;
vector<int> degree(n);
for(auto &edge : edges) {
edge[0] -= 1;
edge[1] -= 1;
degree[edge[0]] += 1;
degree[edge[1]] += 1;
if(edge[0] > edge[1]) swap(edge[0], edge[1]);
direct[p(edge[0], edge[1])] += 1;
}
vector<int> sortedDegree = degree;
sort(sortedDegree.begin(), sortedDegree.end());
vector<int> answer;
for(auto query : queries) {
int cnt = 0;
for(auto d : degree) {
auto it = upper_bound(sortedDegree.begin(), sortedDegree.end(), query - d);
cnt += n - distance(sortedDegree.begin(), it);
if(d > query - d) cnt -= 1;
}
if(!cnt) {
answer.push_back(0);
continue;
}
cnt >>= 1;
for(auto [pa, c] : direct) {
if(degree[pa.a] + degree[pa.b] <= query) continue;
if(degree[pa.a] + degree[pa.b] - c <= query) cnt -= 1;
}
answer.push_back(cnt);
}
return move(answer);
}
};