2021-03-05 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Matrix Diagonal Sum and leetcode's March LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Matrix Diagonal Sum
Description
Given a square matrix mat, return the sum of the matrix diagonals.
Only include the sum of all the elements on the primary diagonal and all the elements on the secondary diagonal that are not part of the primary diagonal.
Example 1:
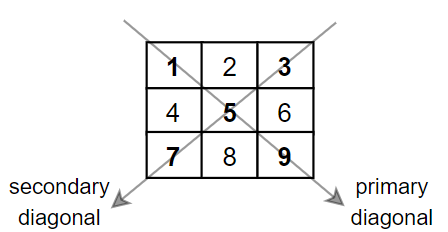
Input: mat = [[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]]
Output: 25
Explanation: Diagonals sum: 1 + 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 25
Notice that element mat[1][1] = 5 is counted only once.
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1]]
Output: 8
Example 3:
Input: mat = [[5]]
Output: 5
Constraints:
n == mat.length == mat[i].length1 <= n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int diagonalSum(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int len = mat.size();
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
sum += mat[i][i] + mat[i][len - 1 - i];
}
if(len & 1) sum -= mat[len/2][len/2];
return sum;
}
};
March LeetCoding Challenge 5
Description
Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given a non-empty binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Input:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Output: [3, 14.5, 11]
Explanation:
The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Note:
- The range of node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
Solution
class Solution {
vector<pair<int, double>> count;
void traversal(TreeNode *root, int level) {
if(!root) return;
if(count.size() <= level) count.push_back(make_pair(0, 0));
count[level].first += 1;
count[level].second += root->val;
traversal(root->left, level + 1);
traversal(root->right, level + 1);
}
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root, 0);
vector<double> answer;
for(auto [cnt, sum] : count) {
answer.push_back(sum / cnt);
}
return move(answer);
}
};