2021-02-10 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Merge In Between Linked Lists and leetcode's February LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Merge In Between Linked Lists
Description
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m respectively.
Remove list1's nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2 in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure incidate the result:
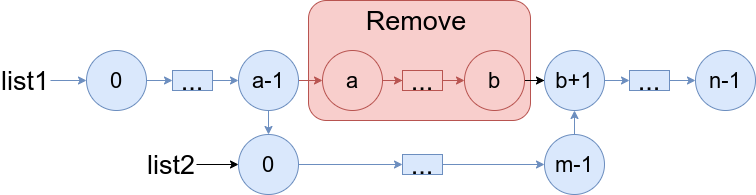
Build the result list and return its head.
Example 1:
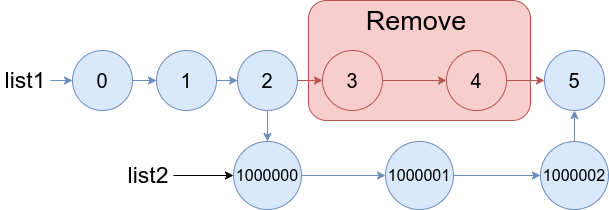
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002]
Output: [0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5]
Explanation: We remove the nodes 3 and 4 and put the entire list2 in their place. The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Example 2:
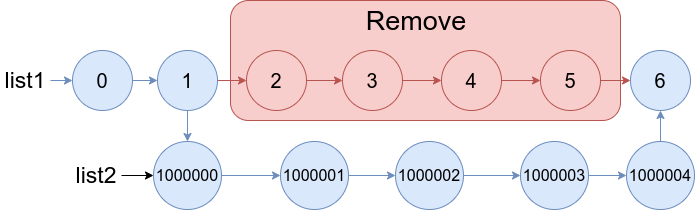
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004]
Output: [0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6]
Explanation: The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Constraints:
- $3 \le list1.length \le 10^4$
1 <= a <= b < list1.length - 1- $1 \le list2.length \le 10^4$
Solution
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode *head = list1;
// find remove position
while(--a && --b) {
list1 = list1->next;
}
ListNode *rest = list1->next;
// link two lists
list1->next = list2;
// move to tail
while(list1->next) list1 = list1->next;
// find rest list1
while(b--) rest = rest->next;
list1->next = rest;
return head;
}
};
February LeetCoding Challenge 10
Description
Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
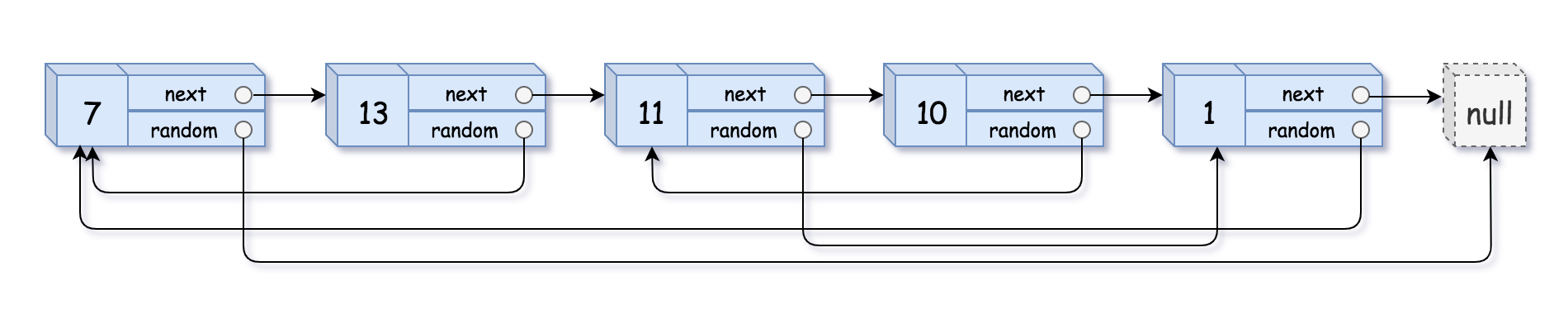
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
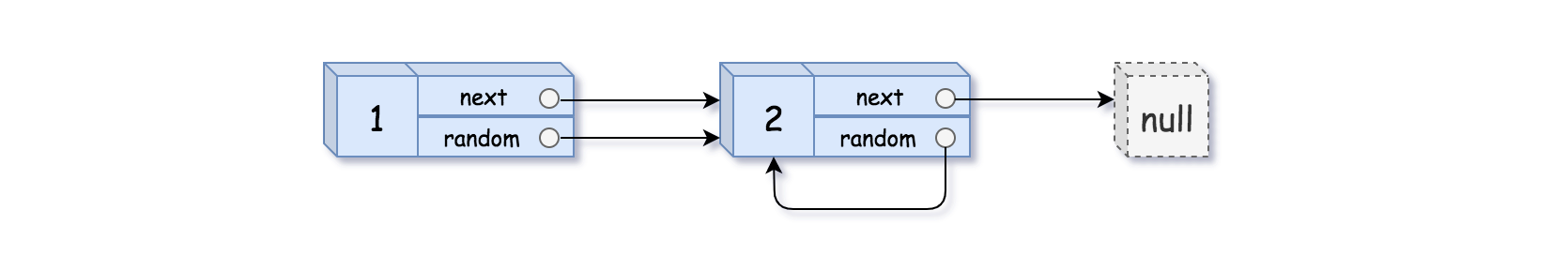
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
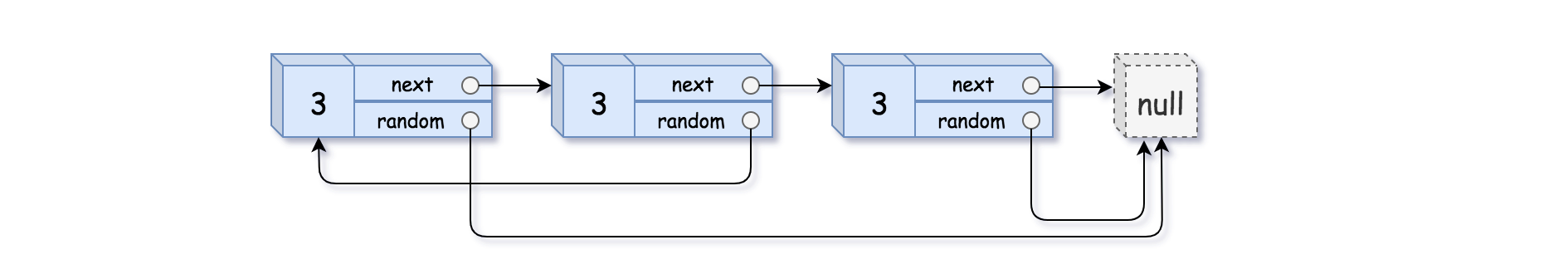
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: The given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
Solution
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
// copy nodes
Node *cur = head;
while(cur) {
Node *newNode = new Node(cur->val);
newNode->next = cur->next;
newNode->random = cur->random;
cur->next = newNode;
cur = newNode->next;
}
// fix random
cur = head;
while(cur) {
cur = cur->next;
if(cur->random) cur->random = cur->random->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
// separate two list
Node *newHead = head->next;
cur = head;
Node *newCur = newHead;
while(cur) {
cur->next = newCur->next;
cur = cur->next;
newCur->next = cur ? cur->next : nullptr;
newCur = newCur->next;
}
return newHead;
}
};