2021-02-09 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Get Watched Videos by Your Friends and leetcode's February LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Get Watched Videos by Your Friends
Description
There are n people, each person has a unique id between 0 and n-1. Given the arrays watchedVideos and friends, where watchedVideos[i] and friends[i] contain the list of watched videos and the list of friends respectively for the person with id = i.
Level 1 of videos are all watched videos by your friends, level 2 of videos are all watched videos by the friends of your friends and so on. In general, the level k of videos are all watched videos by people with the shortest path exactly equal to k with you. Given your id and the level of videos, return the list of videos ordered by their frequencies (increasing). For videos with the same frequency order them alphabetically from least to greatest.
Example 1:
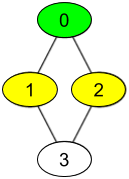
Input: watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 1
Output: ["B","C"]
Explanation:
You have id = 0 (green color in the figure) and your friends are (yellow color in the figure):
Person with id = 1 -> watchedVideos = ["C"]
Person with id = 2 -> watchedVideos = ["B","C"]
The frequencies of watchedVideos by your friends are:
B -> 1
C -> 2
Example 2:
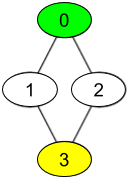
Input: watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 2
Output: ["D"]
Explanation:
You have id = 0 (green color in the figure) and the only friend of your friends is the person with id = 3 (yellow color in the figure).
Constraints:
n == watchedVideos.length == friends.length2 <= n <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i].length <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i][j].length <= 80 <= friends[i].length < n0 <= friends[i][j] < n0 <= id < n1 <= level < n- if
friends[i]containsj, thenfriends[j]containsi
Solution
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> watchedVideosByFriends(vector<vector<string>>& watchedVideos, vector<vector<int>>& friends, int id, int level) {
int len = friends.size();
vector<int> fLevel(len, -1);
queue<int> q;
fLevel[id] = 0;
q.push(id);
unordered_map<string, int> count;
while(!q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto f : friends[cur]) {
if(fLevel[f] == -1) {
fLevel[f] = fLevel[cur] + 1;
q.push(f);
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if(fLevel[i] == level) {
for(auto &v : watchedVideos[i]) count[v] += 1;
}
}
if(count.size() == 0) return vector<string>();
vector<pair<int, string>> result;
for(auto &[s, i] : count) result.push_back(make_pair(i, s));
sort(result.begin(), result.end());
vector<string> answer;
for(auto &[_, s] : result) answer.push_back(s);
return move(answer);
}
};
February LeetCoding Challenge 9
Description
Convert BST to Greater Tree
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note: This question is the same as 1038: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1]
Output: [1,null,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,0,2]
Output: [3,3,2]
Example 4:
Input: root = [3,2,4,1]
Output: [7,9,4,10]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
Solution
in-order traversal
class Solution {
int sum = 0;
void traversal(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root) return;
traversal(root->right);
root->val += sum;
sum = root->val;
traversal(root->left);
}
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root);
return root;
}
};