2021-02-06 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Wildcard Matching and leetcode's February LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Ops, today is Saturday, I need to review the challenge.
BTW, I participated in Biweekly Contest 45.
Wildcard Matching
Description
Given an input string (s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for '?' and '*' where:
'?'Matches any single character.'*'Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).
The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Example 1:
Input: s = "aa", p = "a"
Output: false
Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
Example 2:
Input: s = "aa", p = "*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' matches any sequence.
Example 3:
Input: s = "cb", p = "?a"
Output: false
Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
Example 4:
Input: s = "adceb", p = "*a*b"
Output: true
Explanation: The first '*' matches the empty sequence, while the second '*' matches the substring "dce".
Example 5:
Input: s = "acdcb", p = "a*c?b"
Output: false
Constraints:
0 <= s.length, p.length <= 2000scontains only lowercase English letters.pcontains only lowercase English letters,'?'or'*'.
Solution
class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int sLen = s.length(), sPos = 0;
int pLen = p.length(), pPos = 0;
int starPos = -1, startpPos = -1;
while(sPos < sLen) {
if(pPos < pLen && (p[pPos] == '?' || p[pPos] == s[sPos])) {
sPos += 1;
pPos += 1;
} else if(pPos < pLen && p[pPos] == '*') {
while(pPos < pLen && p[pPos] == '*') pPos += 1;
starPos = sPos;
startpPos = pPos;
} else if(starPos != -1) {
starPos += 1;
sPos = starPos;
pPos = startpPos;
}else return false;
}
// cout << pPos << ' ' << sPos << ' ' << s << ' ' << p << endl;
while(pPos < pLen && p[pPos] == '*') pPos += 1;
return pPos == pLen;
}
};
February LeetCoding Challenge 6
Description
Binary Tree Right Side View
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Explanation:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---
Solution
class Solution {
vector<int> answer;
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int level) {
if(!root) return;
if(level > answer.size()) answer.push_back(root->val);
traversal(root->right, level + 1);
traversal(root->left, level + 1);
}
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root, 1);
return move(answer);
}
};
Biweekly Contest 45
5657. Sum of Unique Elements
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The unique elements are [1,3], and the sum is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are no unique elements, and the sum is 0.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 15
Explanation: The unique elements are [1,2,3,4,5], and the sum is 15.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1001 <= nums[i] <= 100
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfUnique(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_map<int, int> count;
for(auto i : nums) count[i] += 1;
int answer = 0;
for(auto [n, cnt] : count) if(cnt == 1) answer += n;
return answer;
}
};
5658. Maximum Absolute Sum of Any Subarray
You are given an integer array nums. The absolute sum of a subarray [numsl, numsl+1, ..., numsr-1, numsr] is abs(numsl + numsl+1 + ... + numsr-1 + numsr).
Return the maximum absolute sum of any (possibly empty) subarray of nums.
Note that abs(x) is defined as follows:
- If
xis a negative integer, thenabs(x) = -x. - If
xis a non-negative integer, thenabs(x) = x.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-3,2,3,-4]
Output: 5
Explanation: The subarray [2,3] has absolute sum = abs(2+3) = abs(5) = 5.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,-5,1,-4,3,-2]
Output: 8
Explanation: The subarray [-5,1,-4] has absolute sum = abs(-5+1-4) = abs(-8) = 8.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int maxAbsoluteSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int minPrefix = 100000;
int maxPrefix = -100000;
int prefix = 0;
int answer = 0;
for(auto i : nums) {
prefix += i;
minPrefix = min(minPrefix, prefix);
maxPrefix = max(maxPrefix, prefix);
answer = max(prefix - minPrefix, answer);
answer = max(maxPrefix - prefix, answer);
answer = max(abs(prefix), answer);
}
return answer;
}
};
5659. Minimum Length of String After Deleting Similar Ends
Given a string s consisting only of characters 'a', 'b', and 'c'. You are asked to apply the following algorithm on the string any number of times:
- Pick a non-empty prefix from the string
swhere all the characters in the prefix are equal. - Pick a non-empty suffix from the string
swhere all the characters in this suffix are equal. - The prefix and the suffix should not intersect at any index.
- The characters from the prefix and suffix must be the same.
- Delete both the prefix and the suffix.
Return the minimum length of s after performing the above operation any number of times (possibly zero times).
Example 1:
Input: s = "ca"
Output: 2
Explanation: You can't remove any characters, so the string stays as is.
Example 2:
Input: s = "cabaabac"
Output: 0
Explanation: An optimal sequence of operations is:
- Take prefix = "c" and suffix = "c" and remove them, s = "abaaba".
- Take prefix = "a" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "baab".
- Take prefix = "b" and suffix = "b" and remove them, s = "aa".
- Take prefix = "a" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "".
Example 3:
Input: s = "aabccabba"
Output: 3
Explanation: An optimal sequence of operations is:
- Take prefix = "aa" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "bccabb".
- Take prefix = "b" and suffix = "bb" and remove them, s = "cca".
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105sonly consists of characters'a','b', and'c'.
Solution
be careful with edge cases...
class Solution {
public:
int minimumLength(string s) {
int len = s.length();
int begin = 0;
int end = len-1;
while(begin < end && s[begin] == s[end]) {
char c = s[begin];
begin += 1;
end -= 1;
while(begin < end && s[begin] == c) {
begin += 1;
}
while(begin <= end && s[end] == c) {
end -= 1;
}
}
return end - begin + 1;
}
};
5660. Maximum Number of Events That Can Be Attended II
You are given an array of events where events[i] = [startDayi, endDayi, valuei]. The ith event starts at startDayi and ends at endDayi, and if you attend this event, you will receive a value of valuei. You are also given an integer k which represents the maximum number of events you can attend.
You can only attend one event at a time. If you choose to attend an event, you must attend the entire event. Note that the end day is inclusive: that is, you cannot attend two events where one of them starts and the other ends on the same day.
Return the maximum sum of values that you can receive by attending events.
Example 1:
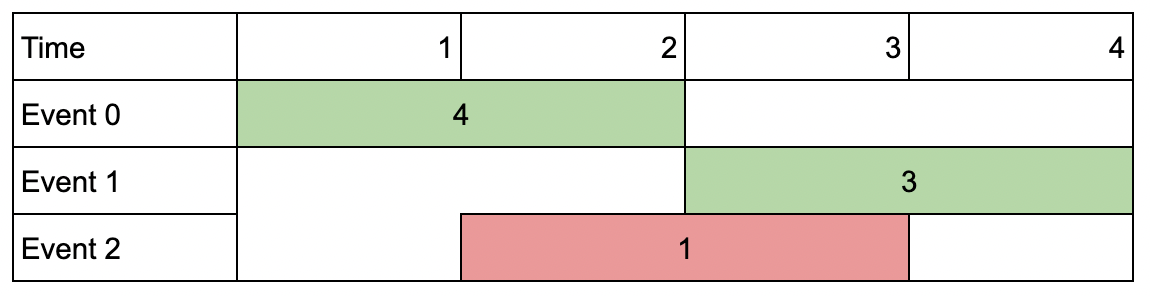
Input: events = [[1,2,4],[3,4,3],[2,3,1]], k = 2
Output: 7
Explanation: Choose the green events, 0 and 1 (0-indexed) for a total value of 4 + 3 = 7.
Example 2:
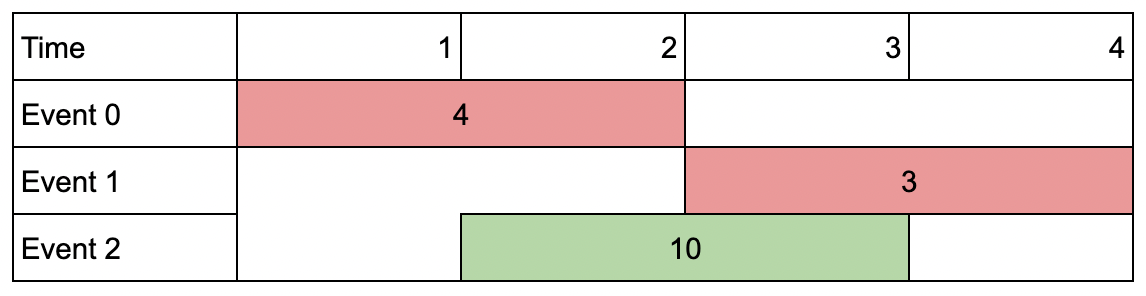
Input: events = [[1,2,4],[3,4,3],[2,3,10]], k = 2
Output: 10
Explanation: Choose event 2 for a total value of 10.
Notice that you cannot attend any other event as they overlap, and that you do not have to attend k events.
Example 3:
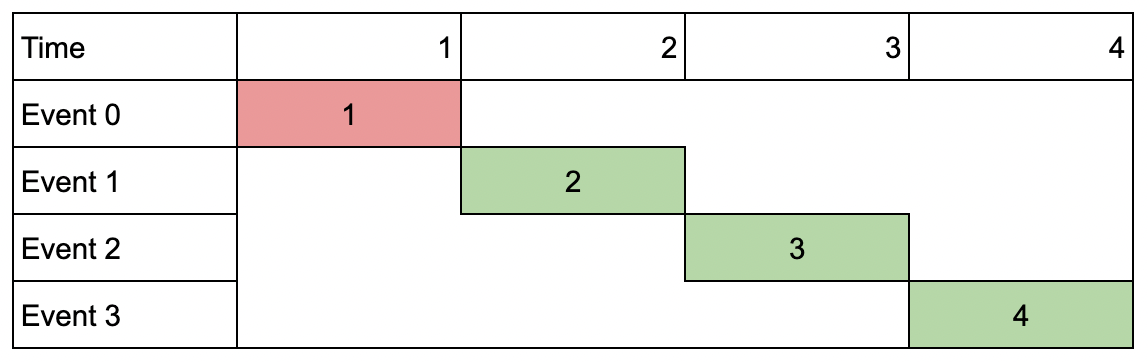
Input: events = [[1,1,1],[2,2,2],[3,3,3],[4,4,4]], k = 3
Output: 9
Explanation: Although the events do not overlap, you can only attend 3 events. Pick the highest valued three.
Constraints:
- $1 \le k \le events.length$
- $1 \le k * events.length \le 10^6$
- $1 \le startDayi \le endDayi \le 10^9$
- $1 \le valuei \le 10^6$
Solution
dp with some enumeration, worst time complexity is $O(k \times events.length^2)$
class Solution {
public:
int maxValue(vector<vector<int>>& events, int k) {
int len = events.size();
vector<int> index(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) index[i] = i;
sort(index.begin(), index.end(), [&](int a, int b) {
return events[a][1] < events[b][1];
});
vector<vector<int>> dp(len, vector<int>(k+2));
vector<int> compatible(len, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if(events[index[j]][1] < events[index[i]][0]) {
compatible[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) dp[i][1] = events[index[i]][2];
for(int i = 2; i <= k; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {
dp[j][i] = dp[j][i-1];
if(compatible[j] != -1) {
for(int pos = compatible[j]; pos >= 0; --pos) {
dp[j][i] = max(dp[j][i], dp[pos][i-1] + events[index[j]][2]);
}
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) answer = max(answer, dp[i][k]);
return answer;
}
};
solution above takes $O(k \times events.length)$ space, but with similar optimization trick used in backpack problem, we can reduce it to $O(events.length)$
class Solution {
public:
int maxValue(vector<vector<int>>& events, int k) {
int len = events.size();
vector<int> index(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) index[i] = i;
sort(index.begin(), index.end(), [&](int a, int b) {
return events[a][1] < events[b][1];
});
vector<int> dp(len);
vector<int> compatible(len, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if(events[index[j]][1] < events[index[i]][0]) {
compatible[i] = j;
break;
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) dp[i] = events[index[i]][2];
for(int i = 1; i < k; ++i) {
for(int j = len-1; j >= 0; --j) {
if(compatible[j] != -1) {
for(int pos = compatible[j]; pos >= 0; --pos) {
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[pos] + events[index[j]][2]);
}
}
}
}
return *max_element(dp.begin(), dp.end());
}
};
LeetCode Review
Check Completeness of a Binary Tree
already done a good job
Integer to English Words
use vector will be faster
class Solution {
const string ZERO = "Zero";
const vector<pair<int, string>> units = {
{ 1000000000, "Billion" },
{ 1000000, "Million" },
{ 1000, "Thousand" },
{ 1, "" }
};
vector<string> ge20 = {
"", // 0
"", // 10
"Twenty",
"Thirty",
"Forty",
"Fifty",
"Sixty",
"Seventy",
"Eighty",
"Ninety"
};
vector<string> lt20 = {
"",
"One",
"Two",
"Three",
"Four",
"Five",
"Six",
"Seven",
"Eight",
"Nine",
"Ten",
"Eleven",
"Twelve",
"Thirteen",
"Fourteen",
"Fifteen",
"Sixteen",
"Seventeen",
"Eighteen",
"Nineteen",
};
string numberLT1000ToWords(int num) {
string result;
if (num >= 100) {
result += lt20[num / 100] + " Hundred";
if (num % 100 == 0) return result;
result += " ";
num %= 100;
}
if (!num) return result;
if (num < 20) {
result += lt20[num];
} else {
result += ge20[num/10];
if (num % 10) result += " " + lt20[num % 10];
}
return result;
}
void numberPartToWords(string &result, int &num, const int threshold, const string &unit) {
if (num >= threshold) {
if (result.length()) result += " ";
result += numberLT1000ToWords(num / threshold);
if (unit.length()) result += " " + unit;
num %= threshold;
}
}
public:
string numberToWords(int num) {
if (!num) return move(ZERO);
string answer = "";
for (const auto &[threshold, unit]: units) {
numberPartToWords(answer, num, threshold, unit);
}
return answer;
}
};
Throne Inheritance
too easy to review
String Compression
too easy to review
Count All Possible Routes
rewrite as memorized dfs, quicker and code is cleaner
class Solution {
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<int>> dp;
int memo(vector<int> &locations, int curCity, int finish, int fuel) {
if(fuel < 0) return 0;
if(dp[curCity][fuel] != -1) return dp[curCity][fuel];
int answer = curCity == finish;
for(int nextCity = 0; nextCity < locations.size(); ++nextCity) {
if(nextCity == curCity) continue;
answer += memo(locations, nextCity, finish, fuel-abs(locations[nextCity] - locations[curCity]));
answer %= MOD;
}
dp[curCity][fuel] = answer;
return answer;
}
public:
int countRoutes(vector<int>& locations, int start, int finish, int fuel) {
int cityLen = locations.size();
dp.resize(cityLen, vector<int>(fuel + 1, -1));
return memo(locations, start, finish, fuel);
}
};
Number of 1 Bits
built-in pop count
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
return __builtin_popcountl(n);
}
};
hand-written naive implementation of pop count
const uint32_t m1 = 0x55555555;
const uint32_t m2 = 0x33333333;
const uint32_t m4 = 0x0F0F0F0F;
const uint32_t m8 = 0x00FF00FF;
const uint32_t m16 = 0x0000FFFF;
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
n = (n & m1) + ((n >> 1) & m1);
n = (n & m2) + ((n >> 2) & m2);
n = (n & m4) + ((n >> 4) & m4);
n = (n & m8) + ((n >> 8) & m8);
n = (n & m16) + ((n >> 16) & m16);
return n;
}
};
Trim a Binary Search Tree
too easy to review
Linked List Cycle
already reviewed
Longest Harmonious Subsequence
sort with binary search
class Solution {
public:
int findLHS(vector<int>& nums) {
int answer = 0;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
auto it = nums.begin();
while(it != nums.end()) {
auto eit = upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), *it+1);
--eit;
if((*eit) - 1 == (*it)) {
int result = distance(it, eit) + 1;
answer = max(answer, result);
}
it = upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), *it);
}
return answer;
}
};
Simplify Path
cleaner code
class Solution {
const string currentDir = "./";
const string currentDirS = ".";
const string upLevel = "../";
const string upLevelS = "..";
public:
string simplifyPath(string path) {
int pos = 0;
int len = path.length();
vector<pair<int, int>> st;
while(pos < len) {
while(pos < len && path[pos] == '/') pos += 1;
auto testUp = path.substr(pos, 3);
if(testUp == upLevel || testUp == upLevelS) {
if(st.size()) st.pop_back();
pos += testUp.length();
continue;
}
auto testCur = path.substr(pos, 2);
if(testCur == currentDir || testCur == currentDirS) {
pos += testCur.length();
continue;
}
int begin = pos;
while(pos < len && path[pos] != '/') pos += 1;
if(pos != begin) st.push_back(make_pair(begin, pos - begin));
}
if(st.empty()) return "/";
string answer;
for(auto [begin, len] : st) answer += '/' + path.substr(begin, len);
return answer;
}
};