2021-01-23 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's January LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
BTW, I participated in Biweekly Contest 44.
LeetCode Review
Regular Expression Matching
more elegant
class Solution {
int lenS;
int lenP;
string source;
string pattern;
bool match(char s, char p) {
return p == '.' || s == p;
}
bool helper(int s, int p) {
if(s == lenS) {
while(p < lenP-1 && pattern[p+1] == '*') p += 2;
return p == lenP;
}
if(p == lenP) return s == lenS;
if(p == lenP - 1 || pattern[p+1] != '*') {
if(match(source[s], pattern[p])) {
return helper(s+1, p+1);
}
return false;
} else {
int pos = s;
do {
if(helper(pos, p+2)) return true;
} while(pos < lenS && match(source[pos++], pattern[p]));
}
return false;
}
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
source = s;
pattern = p;
lenS = s.length();
lenP = p.length();
return helper(0, 0);
}
};
Count The Repetitions
class Solution {
public:
int getMaxRepetitions(string s1, int n1, string s2, int n2) {
int len1 = s1.length();
int len2 = s2.length();
if(len1 * n1 < len2 * n2) return 0;
vector<int> indexChar(len2+1);
vector<int> count(len2+1);
int index = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < min(len2+1, n1); ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < len1; ++j) {
index += (s1[j] == s2[index]);
if(index == len2) {
index = 0;
cnt += 1;
}
}
indexChar[i] = index;
count[i] = cnt;
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if(indexChar[j] == index) {
// cout << i << ' ' << count[j] << ' ' << cnt << endl;
int beforeLoop = count[j];
int loop = (cnt - count[j]) * ((n1 - 1 - j) / (i - j));
int afterLoop = count[(n1 - 1 - j) % (i - j) + j] - count[j];
// cout << beforeLoop << ' ' << loop << ' ' << afterLoop;
return (beforeLoop + loop + afterLoop) / n2;
}
}
}
return count[n1-1] / n2;
}
};
Maximum Number of Non-Overlapping Substrings
class Solution {
int l[128] = {0};
int r[128] = {0};
int getRight(string &s, int left) {
int right = r[s[left]];
for(int i = left; i < right; ++i) {
int c = s[i];
if(l[c] < left) return -1;
right = max(right, r[c]);
}
return right;
}
void init(string &s) {
memset(l, 0x3f, sizeof(l));
memset(r, 0x3f, sizeof(r));
int len = s.length();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int c = s[i];
l[c] = min(i, l[c]);
r[c] = i;
}
}
public:
vector<string> maxNumOfSubstrings(string s) {
int len = s.length();
init(s);
int right = -1;
vector<string> answer;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if(i == l[s[i]]) {
int currentRight = getRight(s, i);
// cout << i << right << currentRight << endl;;
if(currentRight == -1) continue;
if(currentRight < right) answer.back() = s.substr(i, currentRight-i+1);
else answer.push_back(s.substr(i, currentRight-i+1));
right = currentRight;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
Valid Parentheses
too easy to review
Longest Palindromic Substring
still dp, optimization seems not working
class Solution {
vector<vector<bool>> memo;
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int len = s.length();
memo.resize(len+1, vector<bool>(len+1));
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
memo[i][i] = true;
memo[i][i+1] = true;
}
int answer = 1;
int begin = 0;
int lastfound = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= len; ++i) {
bool found = false;
for(int j = 0; j+i <= len; ++j) {
if(memo[j+1][j+i-1] && s[j] == s[j+i-1]) {
memo[j][j+i] = true;
answer = i;
begin = j;
found = true;
lastfound = i;
}
}
if(!found && i == lastfound+2) break;
}
return s.substr(begin, answer);
}
};
find the string by expanding palindrome
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int len = s.length();
int answer = 1;
int begin = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int left = i, right = i;
while(left > 0 && right < len && s[left-1] == s[right]) {
left -= 1;
right += 1;
}
if(right - left > answer) {
answer = right - left;
begin = left;
}
left = i, right = i;
while(left >= 0 && right < len && s[left] == s[right]) {
left -= 1;
right += 1;
}
if(right - left - 1 > answer) {
answer = right - left - 1;
begin = left + 1;
}
}
return s.substr(begin, answer);
}
};
Max Number of K-Sum Pairs
too easy to review
All Possible Full Binary Trees
less code make slower result
class Solution {
vector<vector<TreeNode*>> FBTs;
void generateFBTs(int N) {
FBTs.resize(N+1);
FBTs[1].push_back(new TreeNode(0));
for(int i = 3; i <= N; i += 2) {
for(int j = 1; j < i; j += 2) {
for(auto left : FBTs[j]) {
for(auto right: FBTs[i-j-1]) {
FBTs[i].push_back(new TreeNode(0, deepcopy(left), deepcopy(right)));
}
}
}
}
}
TreeNode* deepcopy(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root) return nullptr;
return new TreeNode(0, deepcopy(root->left), deepcopy(root->right));
}
public:
vector<TreeNode*> allPossibleFBT(int N) {
if(N % 2 == 0) return vector<TreeNode*>();
generateFBTs(N);
return FBTs[N];
}
};
Flip Equivalent Binary Trees
too easy to review
Number of Segments in a String
too easy to review
To Lower Case
too easy to review
Determine if Two Strings Are Close
too easy to review
Predict the Winner
better DP
class Solution {
public:
bool PredictTheWinner(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(len, vector<int>(len));
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
dp[i][i] = nums[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j+i < len; ++j) {
dp[j][j+i] = max(nums[j]-dp[j+1][j+i], nums[j+i]-dp[j][j+i-1]);
}
}
return dp[0][len-1] >= 0;
}
};
Find the Most Competitive Subsequence
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> mostCompetitive(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> monoStack;
int len = nums.size();
vector<int> nextLess(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
while(monoStack.size() + (len - i) > k && monoStack.size() && monoStack.back() > nums[i]) monoStack.pop_back();
monoStack.push_back(nums[i]);
}
while(monoStack.size() > k) monoStack.pop_back();
return move(monoStack);
}
};
January LeetCoding Challenge 23
Description
Sort the Matrix Diagonally
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix's end. For example, the matrix diagonal starting from mat[2][0], where mat is a 6 x 3 matrix, includes cells mat[2][0], mat[3][1], and mat[4][2].
Given an m x n matrix mat of integers, sort each matrix diagonal in ascending order and return the resulting matrix.
Example 1:
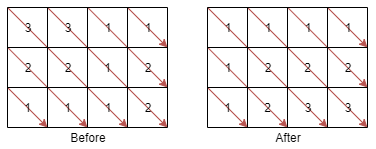
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]]
Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solution
bubble sort
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> diagonalSort(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int rows = mat.size();
int cols = mat.front().size();
for(int i = 0; i < rows+cols-1; ++i) {
int rowBegin = max(0, i+1-cols);
int colBegin = rowBegin == 0 ? cols - 1 - i : 0;
// cout << '#' << rowBegin << ' ' << colBegin << endl;
for(int index = 0; rowBegin + index < rows-1 && colBegin + index < cols-1; ++index) {
for(int j = 1; rowBegin + j < rows-index && colBegin + j < cols-index; ++j) {
// cout << rowBegin + j << ' ' << colBegin + j << endl;
if(mat[rowBegin+j][colBegin+j] < mat[rowBegin+j-1][colBegin+j-1]) {
swap(mat[rowBegin+j][colBegin+j], mat[rowBegin+j-1][colBegin+j-1]);
}
}
}
}
return move(mat);
}
};
Biweekly Contest 44
5645. Find the Highest Altitude
There is a biker going on a road trip. The road trip consists of n + 1 points at different altitudes. The biker starts his trip on point 0 with altitude equal 0.
You are given an integer array gain of length n where gain[i] is the net gain in altitude between points i and i + 1 for all (0 <= i < n). Return the highest altitude of a point.
Example 1:
Input: gain = [-5,1,5,0,-7]
Output: 1
Explanation: The altitudes are [0,-5,-4,1,1,-6]. The highest is 1.
Example 2:
Input: gain = [-4,-3,-2,-1,4,3,2]
Output: 0
Explanation: The altitudes are [0,-4,-7,-9,-10,-6,-3,-1]. The highest is 0.
Constraints:
n == gain.length1 <= n <= 100-100 <= gain[i] <= 100
Solution
nothing to say
class Solution {
public:
int largestAltitude(vector<int>& gain) {
int a = 0;
int answer = 0;
for(auto i : gain) {
a += i;
answer = max(a, answer);
}
return answer;
}
};
5646. Minimum Number of People to Teach
On a social network consisting of m users and some friendships between users, two users can communicate with each other if they know a common language.
You are given an integer n, an array languages, and an array friendships where:
- There are
nlanguages numbered1throughn, languages[i]is the set of languages theithuser knows, andfriendships[i] = [ui, vi]denotes a friendship between the usersuiandvi.
You can choose one language and teach it to some users so that all friends can communicate with each other. Return the minimum number of users you need to teach.
Note that friendships are not transitive, meaning if x is a friend of y and y is a friend of z, this doesn't guarantee that x is a friend of z.
Example 1:
Input: n = 2, languages = [[1],[2],[1,2]], friendships = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: You can either teach user 1 the second language or user 2 the first language.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, languages = [[2],[1,3],[1,2],[3]], friendships = [[1,4],[1,2],[3,4],[2,3]]
Output: 2
Explanation: Teach the third language to users 1 and 2, yielding two users to teach.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 500languages.length == m1 <= m <= 5001 <= languages[i].length <= n1 <= languages[i][j] <= n1 <= ui < vi <= languages.length1 <= friendships.length <= 500- All tuples
(ui, vi)are unique languages[i]contains only unique values
Solution
I misunderstand the problem, so just done it at 1:21:44
class Solution {
public:
int minimumTeachings(int n, vector<vector<int>>& languages, vector<vector<int>>& friendships) {
int m = languages.size();
vector<unordered_set<int>> lang(m+1);
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
lang[i+1] = unordered_set<int>(languages[i].begin(), languages[i].end());
}
vector<bool> sat;
for(auto &f : friendships) {
bool s = false;
for(auto l : lang[f[0]]) {
if(lang[f[1]].count(l)) {
sat.push_back(true);
s = true;
break;
}
}
if(!s) sat.push_back(false);
}
int answer = m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < friendships.size(); ++j) {
if(sat[j]) continue;
// cout << friendships[j][0] << ' ' << friendships[j][1] << endl;
cnt += !lang[friendships[j][0]].count(i);
cnt += !lang[friendships[j][1]].count(i);
lang[friendships[j][0]].insert(i);
lang[friendships[j][1]].insert(i);
}
answer = min(answer, cnt);
}
return answer;
}
};
5647. Decode XORed Permutation
There is an integer array perm that is a permutation of the first n positive integers, where n is always odd.
It was encoded into another integer array encoded of length n - 1, such that encoded[i] = perm[i] XOR perm[i + 1]. For example, if perm = [1,3,2], then encoded = [2,1].
Given the encoded array, return the original array perm. It is guaranteed that the answer exists and is unique.
Example 1:
Input: encoded = [3,1]
Output: [1,2,3]
Explanation: If perm = [1,2,3], then encoded = [1 XOR 2,2 XOR 3] = [3,1]
Example 2:
Input: encoded = [6,5,4,6]
Output: [2,4,1,5,3]
Constraints:
3 <= n < 105nis odd.encoded.length == n - 1
Solution
bitwise magic, haha, I like it.
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> decode(vector<int>& encoded) {
int len = encoded.size() + 1;
vector<int> answer(len);
int exp = 0;
while((1 << exp) < len) {
for(int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
if(encoded[i-1] & (1<<exp)) answer[i] |= (((1<<exp) & answer[i-1]) ^ (1<<exp));
else answer[i] |= ((1<<exp) & answer[i-1]);
}
int oneCnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if((answer[i] & (1<<exp))) oneCnt += 1;
}
int needOne = (len+1) / (1<<(exp+1)) * (1 << exp) + max((len+1) % (1<<(exp+1)) - (1 << exp), 0);
if(needOne != oneCnt) {
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) answer[i] ^= (1<<exp);
}
exp += 1;
}
return answer;
}
};