2021-01-21 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Number of Segments in a String, Flip Equivalent Binary Trees and leetcode's January LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Number of Segments in a String
Description
You are given a string s, return the number of segments in the string.
A segment is defined to be a contiguous sequence of non-space characters.
Example 1:
Input: s = "Hello, my name is John"
Output: 5
Explanation: The five segments are ["Hello,", "my", "name", "is", "John"]
Example 2:
Input: s = "Hello"
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: s = "love live! mu'sic forever"
Output: 4
Example 4:
Input: s = ""
Output: 0
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 300sconsists of lower-case and upper-case English letters, digits or one of the following characters"!@#$%^&*()_+-=',.:".- The only space character in
sis' '.
Solution
class Solution {
public:
int countSegments(string s) {
bool hasSpace = true;
int answer = 0;
for(auto c : s) {
if(c != ' ' && hasSpace) {
hasSpace = false;
answer += 1;
} else if (c == ' ') {
hasSpace = true;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
Flip Equivalent Binary Trees
Description
For a binary tree T, we can define a flip operation as follows: choose any node, and swap the left and right child subtrees.
A binary tree X is flip equivalent to a binary tree Y if and only if we can make X equal to Y after some number of flip operations.
Given the roots of two binary trees root1 and root2, return true if the two trees are flip equivelent or false otherwise.
Example 1:
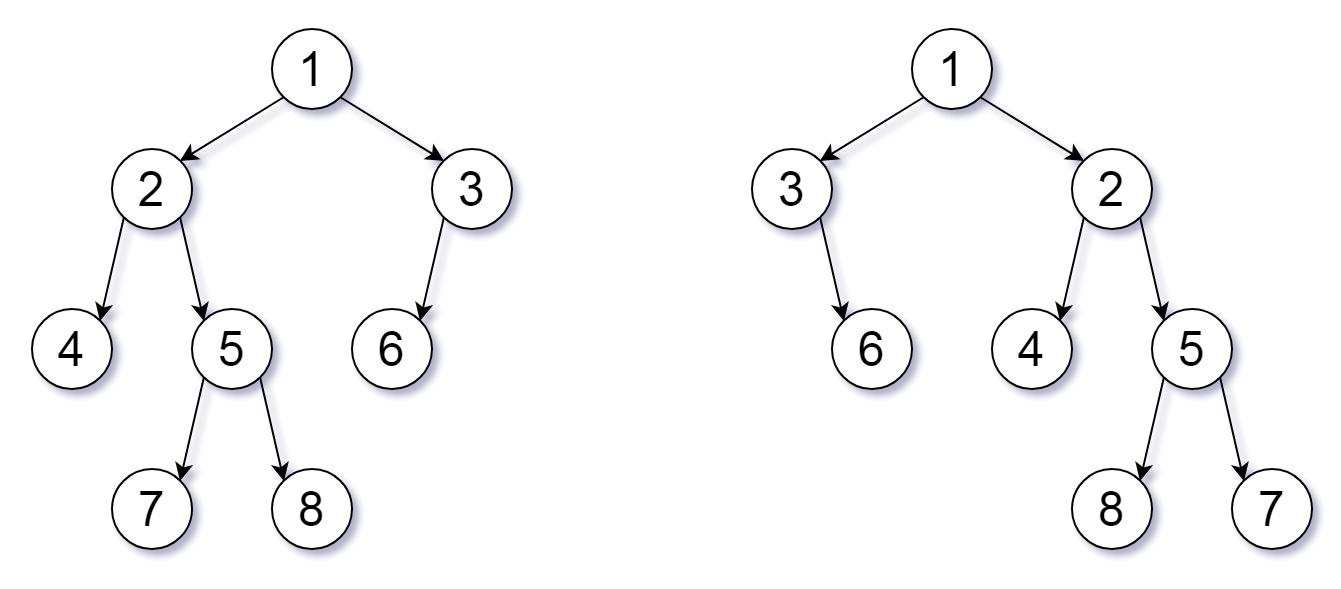
Input: root1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8], root2 = [1,3,2,null,6,4,5,null,null,null,null,8,7]
Output: true
Explanation: We flipped at nodes with values 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = []
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [1]
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: root1 = [0,null,1], root2 = []
Output: false
Example 5:
Input: root1 = [0,null,1], root2 = [0,1]
Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[0, 100]. - Each tree will have unique node values in the range
[0, 99].
Solution
class Solution {
public:
bool flipEquiv(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if((!root1 && root2) || (root1 && !root2)) return false;
if(!root1 && !root2) return true;
if(root1->val != root2->val) return false;
return (flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->left) && flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->right)) ||
(flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->left) && flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->right));
}
};
January LeetCoding Challenge 21
Description
Find the Most Competitive Subsequence
Given an integer array nums and a positive integer k, return the most competitive subsequence of nums of size k.
An array's subsequence is a resulting sequence obtained by erasing some (possibly zero) elements from the array.
We define that a subsequence a is more competitive than a subsequence b (of the same length) if in the first position where a and b differ, subsequence a has a number less than the corresponding number in b. For example, [1,3,4] is more competitive than [1,3,5] because the first position they differ is at the final number, and 4 is less than 5.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,5,2,6], k = 2
Output: [2,6]
Explanation: Among the set of every possible subsequence: {[3,5], [3,2], [3,6], [5,2], [5,6], [2,6]}, [2,6] is the most competitive.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,3,3,5,4,9,6], k = 4
Output: [2,3,3,4]
Constraints:
- $1 <= nums.length <= 10^5$
- $0 <= nums[i] <= 10^9$
1 <= k <= nums.length
Solution
solved but not good enough
class Solution {
map<int, set<int>> mp;
public:
vector<int> mostCompetitive(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int len = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) mp[nums[i]].insert(i);
vector<int> answer(k);
int last = -1;
int cnt = 0;
while(cnt < k) {
bool added = false;
for(auto &[num, st] : mp) {
if(added) break;
for(auto pos : st) {
if(len - pos < k - cnt || last > pos) continue;
if(len - pos > k - cnt) {
answer[cnt] = num;
cnt += 1;
last = pos;
st.erase(pos);
added = true;
} else if(len - pos == k - cnt) {
added = true;
copy(nums.begin() + pos, nums.end(), answer.begin()+cnt);
cnt += len - pos;
}
break;
}
if(st.empty()) mp.erase(num);
}
}
return answer;
}
};