2020-12-12 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's November LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
LeetCode Review
Jump Game II
smaller constant $O(n)$ solution
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
if(len == 1) return 0;
if(len-1 <= nums[0]) return 1;
int farthest = -1;
int nextJump = nums[0];
int jump = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
farthest = max(farthest, i + nums[i]);
if(i == nextJump) {
jump += 1;
nextJump = farthest;
}
if(nextJump >= len-1) break;
}
return jump;
}
};
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
use just one variable for position
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
if(len < 3) return len;
int removePos = 2;
int pos = 1;
for( ;removePos < len; ++removePos, ++pos) {
while(removePos < len && nums[removePos] == nums[pos-1]) removePos +=1;
if(removePos == len) break;
swap(nums[pos+1], nums[removePos]);
}
nums.resize(pos+1);
return pos+1;
}
};
Path with Maximum Probability
bellman ford algorithm
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
vector<double> distance(n);
distance[start] = 1;
int len = edges.size();
for(int loop = 0; loop < len; ++loop) {
bool modified = false;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int a = edges[i][0];
int b = edges[i][1];
double prob = succProb[i];
if(distance[b]*prob > distance[a]) {
distance[a] = distance[b]*prob;
modified = true;
}
if(distance[a]*prob > distance[b]) {
distance[b] = distance[a]*prob;
modified = true;
}
}
if(!modified) break;
}
return distance[end];
}
};
Valid Mountain Array
nothing to say
class Solution {
public:
bool validMountainArray(vector<int>& arr) {
int len = arr.size();
if(len < 3 || arr[1] <= arr[0]) return false;
int pos = 1;
while(pos < len && arr[pos] > arr[pos-1]) ++pos;
if(pos == len) return false;
while(pos < len && arr[pos] < arr[pos-1]) ++pos;
return pos == len;
}
};
Distinct Subsequences
$$ dp[i][j] = \begin{cases} dp[i-1][j] & \text{if s[i] != t[j]}\ dp[i-1][j] + dp[i-1][j-1] & \text{if s[i] == t[j]} \end{cases} $$
using same optimization techniques as backpack problem then we only need one dimension vector.
class Solution {
public:
int numDistinct(string s, string t) {
int slen = s.length();
int tlen = t.length();
if(slen <= tlen) return s == t;
vector<long long> dp(tlen+1);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < slen; ++i) {
int beginPos = max(1, tlen-slen+i);
int endPos = min(tlen, i+slen-tlen+1);
for(int j = endPos; j >= beginPos; --j) {
if(s[i] == t[j-1]) dp[j] += dp[j-1];
}
}
return dp.back();
}
};
Distinct Subsequences II
nothing to say
class Solution {
public:
int distinctSubseqII(string S) {
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
vector<int> last(26, -1);
int len = S.length();
vector<int> dp(len+1);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= len; ++i) {
int c = S[i-1] - 'a';
dp[i] = 2 * dp[i-1];
dp[i] %= MOD;
if(last[c] != -1) {
dp[i] -= dp[last[c]-1];
if(dp[i] < 0) dp[i] += MOD;
}
last[c] = i;
}
return dp.back()-1;
}
};
Binary Search Tree Iterator
morris traversal
class BSTIterator {
TreeNode *cur, *prev;
public:
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
cur = root, prev = nullptr;
}
int next() {
int result = -1;
while(result < 0) {
if(!cur->left) {
result = cur->val;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->right;
} else {
TreeNode *pred = cur->left;
while(pred->right && pred->right != cur) pred = pred->right;
if(pred->right) {
pred->right = nullptr;
result = cur->val;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->right;
} else {
pred->right = cur;
cur = cur->left;
}
}
}
return result;
}
bool hasNext() {
return cur;
}
};
Minimum Moves to Make Array Complementary
sweeping line
class Solution {
public:
int minMoves(vector<int>& nums, int limit) {
vector<int> lines(2*limit+2);
int len = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i*2 < len; ++i) {
int mmin = min(nums[i], nums[len-1-i]);
int mmax = max(nums[i], nums[len-1-i]);
lines[mmin+1] -= 1;
lines[mmin+mmax] -= 1;
lines[mmin+mmax+1] += 1;
lines[mmax+limit+1] += 1;
}
int current = len;
int answer = INT_MAX;
for(auto i : lines) {
current += i;
answer = min(answer, current);
}
return answer;
}
};
Smallest Rotation with Highest Score
add some comment
class Solution {
public:
int bestRotation(vector<int>& A) {
int len = A.size();
vector<int> lines(len);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int leastRotate = (i + 1) % len;
// most rotate is i - A[i] + len, plus one is offset for line
int mostRotate = (i - A[i] + len + 1) % len;
lines[leastRotate] += 1;
lines[mostRotate] -= 1;
if(leastRotate > mostRotate-1) {
// rotate range is like [0,1]+[4,5]
lines[0] += 1;
}
}
int current = 0;
int highScore = 0;
int answer = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
current += lines[i];
if(current > highScore) {
highScore = current;
answer = i;
}
}
return answer;
}
};
Reduce Array Size to The Half
using vector is slower
class Solution {
public:
int minSetSize(vector<int>& arr) {
if(arr.size() < 3) return 1;
int len = arr.size();
vector<int> cnt(100001);
for(auto i : arr) cnt[i] += 1;
sort(cnt.begin(), cnt.end(), greater<int>());
int c = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 100001; ++i) {
c += cnt[i];
if(c*2 >= len) return i+1;
}
return -1;
}
};
Pairs of Songs With Total Durations Divisible by 60
too easy to review
Spiral Matrix II
already reviewed
December LeetCoding Challenge 12
Description
Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes
Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Note: This question is the same as 1123: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
Example 1:
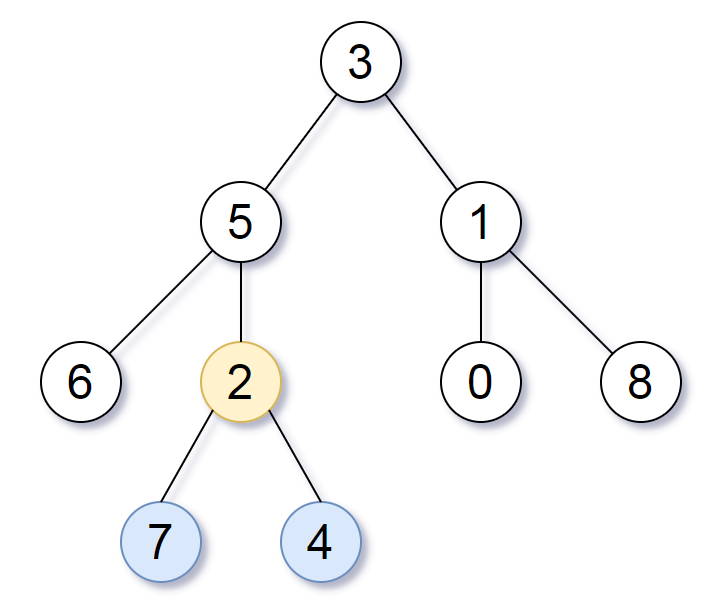
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
Output: [2,7,4]
Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram.
The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree.
Notice that nodes 5, 3 and 2 contain the deepest nodes in the tree but node 2 is the smallest subtree among them, so we return it.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2]
Output: [2]
Explanation: The deepest node in the tree is 2, the valid subtrees are the subtrees of nodes 2, 1 and 0 but the subtree of node 2 is the smallest.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Solution
answer with worst run time and space usage XD
class Solution {
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> parent;
vector<TreeNode*> deepest;
int deepestLevel = -1;
void findDeepestLevel(TreeNode* root, int curLevel) {
if(!root) return;
if(curLevel > deepestLevel) {
deepestLevel = curLevel;
}
parent[root->left] = root;
parent[root->right] = root;
findDeepestLevel(root->left, curLevel+1);
findDeepestLevel(root->right, curLevel+1);
}
void findDeepestNodes(TreeNode* root, int curLevel) {
if(!root) return;
if(curLevel == deepestLevel) {
deepest.push_back(root);
} else {
findDeepestNodes(root->left, curLevel+1);
findDeepestNodes(root->right, curLevel+1);
}
}
public:
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return root;
findDeepestLevel(root, 0);
findDeepestNodes(root, 0);
if(deepest.size() == 1) return deepest.front();
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> cur;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> nxt;
for(auto node : deepest) {
cur[parent[node]] += 1;
}
while(cur.size() > 1) {
nxt.clear();
for(auto [node, _] : cur) {
nxt[parent[node]] += 1;
}
cur = nxt;
}
return cur.begin()->first;
}
};