2020-12-03 Daily-Challenge
Today I have done Sort the Matrix Diagonally and Merge k Sorted Lists on leetcode and leetcode's December LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
Sort the Matrix Diagonally
Description
Given a m * n matrix mat of integers, sort it diagonally in ascending order from the top-left to the bottom-right then return the sorted array.
Example 1:
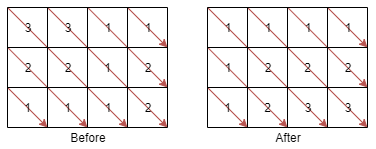
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]]
Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solution
this problem is so... disgusting
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> diagonalSort(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int h = mat.size();
int w = mat[0].size();
vector<int> index;
for(int i = 0; i < h+w-1; ++i) {
int beginH = i >= w ? i-w+1 : 0;
int endH = beginH ? (i+w-1 < h ? i+w-1 : h-1) : min(i, h-1);
// cout << beginH << ' ' << endH << endl;
if(beginH == endH) continue;
index.clear();
for(int j = beginH; j <= endH; ++j) {
index.push_back(mat[j][j+w-1-i]);
}
sort(index.begin(), index.end());
for(int j = beginH; j <= endH; ++j) {
mat[j][j+w-1-i] = index[j-beginH];
}
}
return mat;
}
};
Merge k Sorted Lists
Description
You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.
Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
Example 1:
Input: lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
Explanation: The linked-lists are:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
merging them into one sorted list:
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
Example 2:
Input: lists = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: lists = [[]]
Output: []
Constraints:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]is sorted in ascending order.- The sum of
lists[i].lengthwon't exceed10^4.
Solution
nothing to say
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, bool(*)(ListNode*, ListNode*)> q([](ListNode* a, ListNode* b){
return a->val > b->val;
});
if(lists.empty()) return nullptr;
ListNode* newHead = new ListNode(-100100);
ListNode* cur = newHead;
for(auto list: lists) {
if(list) q.push(list);
}
while(q.size()) {
cur->next = q.top();
q.pop();
cur = cur->next;
if(cur->next) q.push(cur->next);
}
return newHead->next;
}
};
December LeetCoding Challenge 3
Description
Increasing Order Search Tree
Given the root of a binary search tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only one right child.
Example 1:
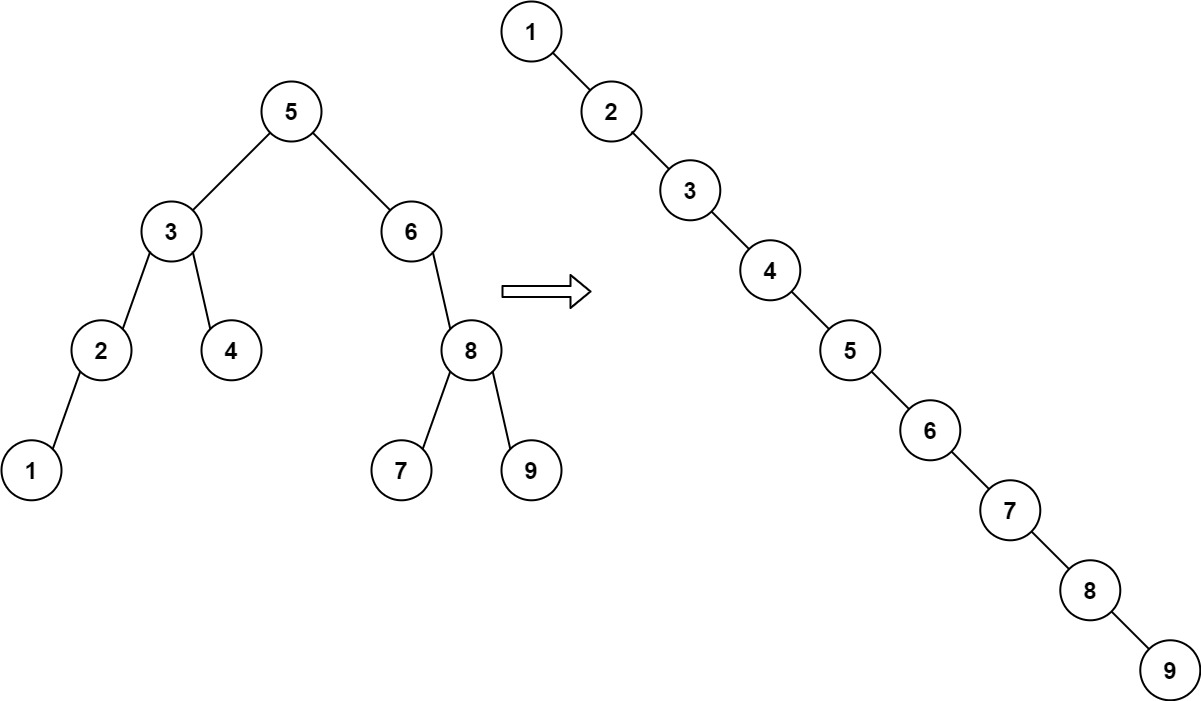
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
Example 2:
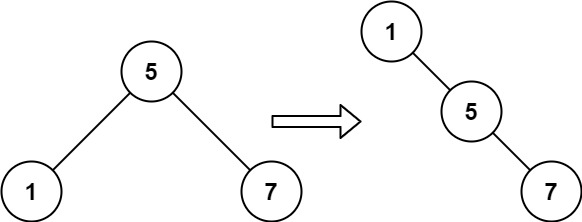
Input: root = [5,1,7]
Output: [1,null,5,null,7]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
inorder traversal is all we need, 'cause it's a BST
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
void helper(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* &newRoot) {
if(!root) return;
helper(root->left, newRoot);
newRoot->right = new TreeNode(root->val);
newRoot = newRoot->right;
helper(root->right, newRoot);
}
public:
TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* newRootHead = new TreeNode(-1);
TreeNode* helperNode = newRootHead;
helper(root, helperNode);
return newRootHead->right;
}
};