2020-11-08 Daily-Challenge
Today is Sunday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's November LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
BTW I decided to write solution directly on website rather than on VSCode when reviewing.
LeetCode Review
Minimum Height Trees
BFS by degree
class Solution {
vector<unordered_set<int>> neighbors;
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
if(n == 1) return vector<int>{0};
neighbors = vector<unordered_set<int>>(n);
for(auto &edge : edges) {
neighbors[edge[0]].insert(edge[1]);
neighbors[edge[1]].insert(edge[0]);
}
vector<int> current, next;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(neighbors[i].size() == 1) {
next.push_back(i);
}
}
while(next.size()) {
current = next;
next.clear();
for(auto n : current) {
for(auto neighbor : neighbors[n]) {
neighbors[neighbor].erase(n);
if(neighbors[neighbor].size() == 1) next.push_back(neighbor);
}
}
}
return current;
}
};
tree DP
class Solution {
vector<int> height1, height2, dp;
vector<vector<int>> neighbors;
void heightDFS(int current, int parent) {
height1[current] = height2[current] = -1;
for(auto neighbor : neighbors[current]) {
if(neighbor == parent) continue;
heightDFS(neighbor, current);
int heightFromNeighbor = height1[neighbor] + 1;
if(heightFromNeighbor > height1[current]) {
height2[current] = height1[current];
height1[current] = heightFromNeighbor;
} else if (heightFromNeighbor > height2[current]) {
height2[current] = heightFromNeighbor;
}
}
height1[current] = max(height1[current], 0);
}
void treeDP(int current, int parent, int acc) {
dp[current] = max(height1[current], acc);
for(auto neighbor : neighbors[current]) {
if(neighbor == parent) continue;
int newAcc = max(acc+1, (height1[neighbor] + 1 == height1[current] ? height2[current]: height1[current]) + 1);
treeDP(neighbor, current, newAcc);
}
}
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
height1.resize(n, 0);
height2.resize(n, 0);
dp.resize(n, 0);
neighbors.resize(n, vector<int>());
for(auto edge : edges) {
neighbors[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);
neighbors[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);
}
heightDFS(0, -1);
treeDP(0, -1, 0);
int height = *min_element(dp.begin(), dp.end());
vector<int> answer;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(dp[i] == height) answer.push_back(i);
}
return answer;
}
};
November LeetCoding Challenge 8
Description
Binary Tree Tilt
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of every tree node's tilt.
The tilt of a tree node is the absolute difference between the sum of all left subtree node values and all right subtree node values. If a node does not have a left child, then the sum of the left subtree node values is treated as 0. The rule is similar if there the node does not have a right child.
Example 1:
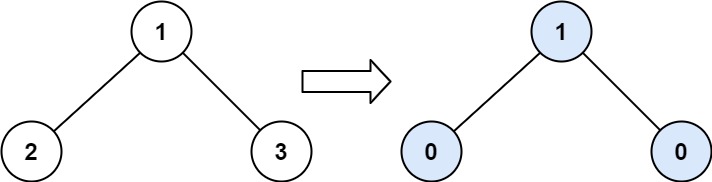
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Tilt of node 2 : |0-0| = 0 (no children)
Tilt of node 3 : |0-0| = 0 (no children)
Tile of node 1 : |2-3| = 1 (left subtree is just left child, so sum is 2; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 3)
Sum of every tilt : 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
Example 2:
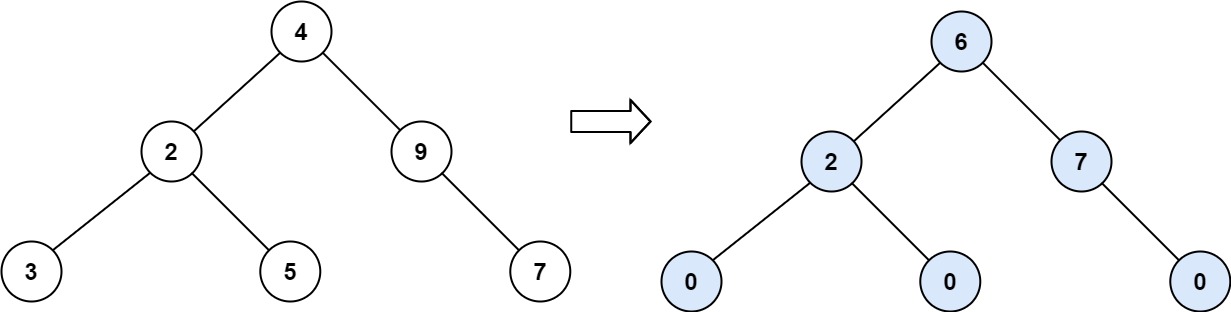
Input: root = [4,2,9,3,5,null,7]
Output: 15
Explanation:
Tilt of node 3 : |0-0| = 0 (no children)
Tilt of node 5 : |0-0| = 0 (no children)
Tilt of node 7 : |0-0| = 0 (no children)
Tilt of node 2 : |3-5| = 2 (left subtree is just left child, so sum is 3; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 5)
Tilt of node 9 : |0-7| = 7 (no left child, so sum is 0; right subtree is just right child, so sum is 7)
Tilt of node 4 : |(3+5+2)-(9+7)| = |10-16| = 6 (left subtree values are 3, 5, and 2, which sums to 10; right subtree values are 9 and 7, which sums to 16)
Sum of every tilt : 0 + 0 + 0 + 2 + 7 + 6 = 15
Example 3:
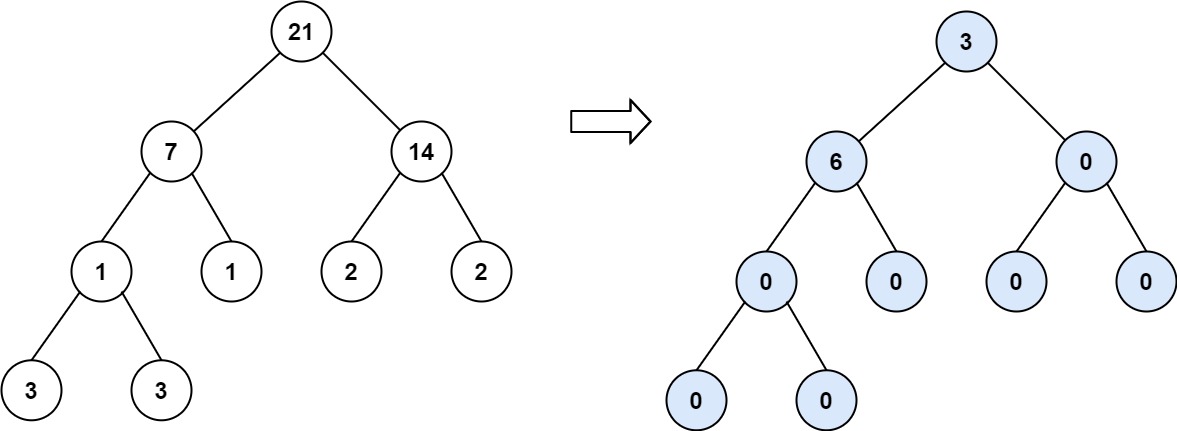
Input: root = [21,7,14,1,1,2,2,3,3]
Output: 9
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
return a pair should be enough
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
pair<int, int> findAnswer(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return make_pair(0, 0);
int curVal = root->val;
auto [leftVal, leftSum] = findAnswer(root->left);
auto [rightVal, rightSum] = findAnswer(root->right);
root->val = abs(leftVal-rightVal);
return make_pair(leftVal+rightVal+curVal, root->val+leftSum+rightSum);
}
public:
int findTilt(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return 0;
auto [tmp, answer] = findAnswer(root);
return answer;
}
};
but we can use a reference instead
class Solution {
int tilt(TreeNode* root, int &answer) {
if(!root) return 0;
int leftVal = tilt(root->left, answer);
int rightVal = tilt(root->right, answer);
answer += abs(leftVal - rightVal);
return leftVal + rightVal + root->val;
}
public:
int findTilt(TreeNode* root) {
int answer = 0;
tilt(root, answer);
return answer;
}
};