2020-10-31 Daily-Challenge
Today is Saturday, I gonna review the tasks I've done this week, and finish today's leetcode's October LeetCoding Challenge with cpp.
BTW I decided to write solution directly on website rather than on VSCode when reviewing.
LeetCode Review
Odd Even Jump
monotonic stack
class Solution {
public:
int oddEvenJumps(vector<int>& A) {
if(A.size() == 1) return 1;
vector<int> index(A.size());
for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); ++i) {
index[i] = A.size()-i-1;
}
stable_sort(index.begin(), index.end(), [A](int a, int b){ return A[a] > A[b];});
stack<int, vector<int>> nonDecresingStack;
vector<int> oddJump(A.size());
for(auto i : index) {
while(nonDecresingStack.size() && i > nonDecresingStack.top()) nonDecresingStack.pop();
oddJump[i] = nonDecresingStack.empty() ? -1 : nonDecresingStack.top();
nonDecresingStack.push(i);
}
stack<int, vector<int>> nonIncreasingStack;
vector<int> evenJump(A.size());
stable_sort(index.begin(), index.end(), [A](int a, int b){ return A[a] < A[b];});
for(auto i : index) {
while(nonIncreasingStack.size() && i > nonIncreasingStack.top()) nonIncreasingStack.pop();
evenJump[i] = nonIncreasingStack.empty() ? -1 : nonIncreasingStack.top();
nonIncreasingStack.push(i);
}
vector<bool> odd(A.size());
vector<bool> even(A.size());
odd[A.size()-1] = true;
even[A.size()-1] = true;
for(int i = A.size()-2; i >= 0; --i) {
if(oddJump[i] != -1) odd[i] = even[oddJump[i]];
if(evenJump[i] != -1) even[i] = odd[evenJump[i]];
}
int ans = 0;
for(bool b : odd) {
ans += b;
}
return ans;
}
};
Number of Islands
dfs
class Solution {
int move[4][2] = {{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
int height;
int width;
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int h, int w) {
grid[h][w] = '0';
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int newH = h + move[i][0];
int newW = w + move[i][1];
if(newH >= 0 && newH < height && newW >= 0 && newW < width &&
grid[newH][newW] == '1') {
dfs(grid, newH, newW);
}
}
}
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
height = grid.size();
width = grid[0].size();
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < height; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < width; ++j) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1') {
ans += 1;
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Count Primes
linear sieve run slower and occupy more memory.
class Solution {
public:
int countPrimes(int n) {
vector<bool> isPrime(n, true);
vector<int> prime;
for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
if(isPrime[i]) {
prime.push_back(i);
}
for(int j = 0; j < prime.size(); ++j) {
if(prime[j] * i >= n) break;
isPrime[i * prime[j]] = false;
if(!(i%prime[j])) break;
}
}
return prime.size();
}
};
Add Digits
another way using associativity
class Solution {
public:
int addDigits(int num) {
while(num > 9) {
num = num % 10 + num / 10;
}
return num;
}
};
Find the Closest Palindrome
more elegant but code is not clean enough to make me happy.
class Solution {
public:
string nearestPalindromic(string n) {
int len = n.length();
set<long long> ans;
long long largest = pow(10, len) + 1;
ans.insert(largest);
long long smallest = pow(10, len-1) - 1;
ans.insert(smallest);
string prefix = string(n.begin(), n.begin()+(len+1)/2);
long long prefixNum = stoll(prefix);
for(int i = -1; i <= 1; ++i) {
long long currentHalf = prefixNum + i;
string currentHalfString = to_string(currentHalf);
string currentString = currentHalfString + string(currentHalfString.rbegin()+(len&1), currentHalfString.rend());
ans.insert(stoll(currentString));
}
long long num = stoll(n);
ans.erase(num);
long long minDiff = LONG_LONG_MAX, answer = 0;
for(auto l : ans) {
if(minDiff > abs(num-l)) {
minDiff = abs(num-l);
answer = l;
}
}
return to_string(answer);
}
};
Champagne Tower
add quick break
class Solution {
public:
double champagneTower(int poured, int query_row, int query_glass) {
vector<double> glasses(query_row+1);
glasses[0] = poured;
for(int i = 0; i < query_row; ++i) {
bool allEmpty = true;
for(int j = i; j >= 0; --j) {
if(glasses[j] > 1) allEmpty = false;
glasses[j+1] += max(0.0, (glasses[j] - 1.0)/2);
glasses[j] = max(0.0, (glasses[j] - 1.0)/2);
}
if(allEmpty) return 0.0;
}
return min(1.0, glasses[query_glass]);
}
};
Number of Longest Increasing Subsequence
class Solution {
public:
int findNumberOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
vector<int> LIS(nums.size(), 1);
vector<int> ways(nums.size(), 1);
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if(nums[j] < nums[i] && LIS[j]+1 > LIS[i]) {
ways[i] = ways[j];
LIS[i] = LIS[j] + 1;
} else if(nums[j] < nums[i] && LIS[j]+1 == LIS[i]) {
ways[i] += ways[j];
}
}
}
int LISLength = *max_element(LIS.begin(), LIS.end());
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if(LIS[i] == LISLength) ans += ways[i];
}
return ans;
}
};
Summary Ranges
nothing to say
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> summaryRanges(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return vector<string>();
vector<string> ans;
int begin = nums[0], end = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if(nums[i] != end+1) {
if(begin == end) ans.push_back(to_string(begin));
else ans.push_back(to_string(begin) + "->" + to_string(end));
begin = nums[i];
end = nums[i];
} else {
end += 1;
}
}
if(begin == end) ans.push_back(to_string(begin));
else ans.push_back(to_string(begin) + "->" + to_string(end));
return ans;
}
};
Maximize Distance to Closest Person
nothing to say
class Solution {
public:
int maxDistToClosest(vector<int>& seats) {
vector<int> left(seats.size());
vector<int> right(seats.size());
int leftLeast = -20000;
for(int i = 0; i < seats.size(); ++i) {
if(!seats[i]) left[i] = i - leftLeast;
else leftLeast = i;
}
int rightLeast = 40000;
for(int i = seats.size()-1; i >= 0; --i) {
if(!seats[i]) right[i] = rightLeast - i;
else rightLeast = i;
}
int dist = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < seats.size(); ++i) {
if(min(left[i], right[i]) > dist) {
dist = min(left[i], right[i]);
}
}
return dist;
}
};
October LeetCoding Challenge 31
Description
Recover Binary Search Tree
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
Example 1:
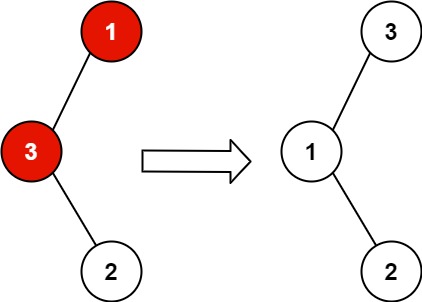
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2]
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
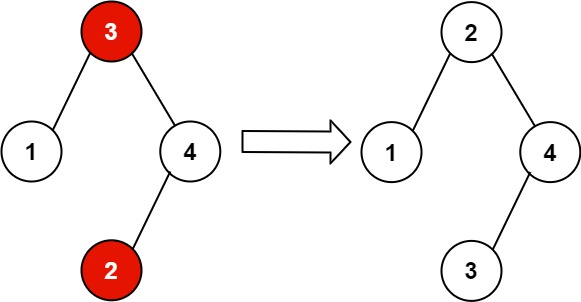
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Solution
At the beginning of challenge, I want to solve it by try to recover left branch of binary tree first then recover right branch, and in the end recover root.
class Solution {
tuple<TreeNode*, TreeNode*, bool> recoverTreeAndGetExtremum(TreeNode *root) {
TreeNode *maxNode, *minNode, *mminNode = nullptr, *mmaxNode = nullptr;
bool fixed;
if(root->left){
tie(maxNode, minNode, fixed) = recoverTreeAndGetExtremum(root->left);
if(fixed) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, true);
if(maxNode->val > root->val) {
swap(root, maxNode);
return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, true);
}
mminNode = minNode;
} else {
mminNode = root;
}
if(root->right) {
tie(maxNode, minNode, fixed) = recoverTreeAndGetExtremum(root->right);
if(fixed) return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, true);
if(minNode->val < root->val) {
swap(root, minNode);
return make_tuple(nullptr, nullptr, true);
}
mmaxNode = maxNode;
} else {
mmaxNode = root;
}
return make_tuple(mminNode, mmaxNode, false);
}
void swap(TreeNode *a, TreeNode *b) {
int tmp = a->val;
a->val = b->val;
b->val = tmp;
}
public:
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return;
if(root->left) {
auto [ minNode, maxNode, fixed ] = recoverTreeAndGetExtremum(root->left);
if(fixed) return;
if(maxNode->val > root->val) {
swap(root, maxNode);
return;
}
}
if(root->right) {
auto [ minNode, maxNode, fixed ] = recoverTreeAndGetExtremum(root->right);
if(fixed) return;
if(minNode->val < root->val) {
swap(root, minNode);
return;
}
}
}
};
The answer goes wrong, because I should know whether root is at the wrong position, then recover branches.
I started to figure out what really matter to this problem. For a tree, there is five possibilities where goes wrong:
- there is a swap happened cross the subtree.
- root node have swap with a node on left subtree.
- root node have swap with a node on right subtree.
- there is a swap happened on the left subtree.
- there is a swap happened on the right subtree.
then what we should do is clear.
class Solution {
bool fixed = false;
void swap(TreeNode *a, TreeNode *b) {
int tmp = a->val;
a->val = b->val;
b->val = tmp;
}
tuple<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> getExtremum(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root) exit(-1);
TreeNode *minNode = root, *maxNode = root;
if(root->left) {
auto [ minLeftNode, maxLeftNode ] = getExtremum(root->left);
if(minLeftNode->val < minNode->val) minNode = minLeftNode;
if(maxLeftNode->val > maxNode->val) maxNode = maxLeftNode;
}
if(root->right) {
auto [ minRightNode, maxRightNode ] = getExtremum(root->right);
if(minRightNode->val < minNode->val) minNode = minRightNode;
if(maxRightNode->val > maxNode->val) maxNode = maxRightNode;
}
return make_tuple(minNode, maxNode);
}
public:
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root || fixed) return;
TreeNode *minRightNode = nullptr, *maxLeftNode = nullptr, *tmp;
if(root->left) tie(tmp, maxLeftNode) = getExtremum(root->left);
if(root->right) tie(minRightNode, tmp) = getExtremum(root->right);
if(maxLeftNode && minRightNode && minRightNode->val < maxLeftNode->val) {
swap(maxLeftNode, minRightNode);
fixed = true;
return;
} else if(maxLeftNode && maxLeftNode->val > root->val) {
swap(maxLeftNode, root);
fixed = true;
return;
} else if(minRightNode && minRightNode->val < root->val) {
swap(minRightNode, root);
fixed = true;
return;
}
if(root->left) recoverTree(root->left);
if(root->right) recoverTree(root->right);
}
};
but it is of O(n) space complexity, morris traversal should be used for O(1) space complexity.
would try tomorrow.